Dubbing, subtitles, and synchronization in video translation have always been technical challenges. This is due to significant differences in grammatical structures and speech rates across languages. When a sentence is translated into another language, the character count and speech speed change, causing the translated dubbing duration to differ from the original audio, leading to misalignment between subtitles, audio, and visuals.
Specific manifestations include: the original speaker has finished talking, but the dubbing is only halfway through; or the next sentence in the original video has already started, while the dubbing is still delivering the previous line.
Character Count Changes Due to Translation
For example, translating the following Chinese sentences into English results in significant changes in length and syllable count, which in turn alters the audio duration:
Chinese: 得国最正莫过于明
English: There is no country more upright than the Ming Dynasty
Chinese: 我一生都在研究宇宙
English: I have been studying the universe all my life
Chinese: 北京圆明园四只黑天鹅疑被流浪狗咬死
English: Four black swans in Beijing's Yuanmingyuan Garden suspected of being bitten to death by stray dogs
As shown, after translating Chinese subtitles into English and dubbing, the dubbed audio duration often exceeds the original Chinese audio duration. To address this issue, several strategies are commonly employed:
Several Coping Strategies
Increase Dubbing Speed: Theoretically, as long as there is no upper limit on speech speed, it is always possible to match the audio duration with the subtitle duration. For example, if the original audio duration is 1 second and the dubbed audio duration is 3 seconds, increasing the dubbing speed to 300% can synchronize them. However, this method makes the speech sound rushed and unnatural, with inconsistent pacing, resulting in suboptimal overall quality.
Simplify the Translation: Shorten the translated text to reduce the dubbing duration. For example, translating "我一生都在研究宇宙" into the more concise "Cosmology is my life's work." While this method yields the best results, it requires manual revision of each subtitle, making it highly inefficient.
Adjust Silence Between Subtitles: If there is silence between two subtitle segments in the original audio, reducing or removing part of the silence can bridge the duration gap. For instance, if there is 2 seconds of silence between two subtitles in the original audio, and the translated first subtitle is 1.5 seconds longer, the silence can be shortened to 0.5 seconds to align the second subtitle's dubbing time with the original audio. However, not all subtitles have sufficient silence to adjust, limiting the applicability of this method.
Remove Silence Before and After Dubbing: Silence is often retained before and after dubbing; removing it can effectively shorten the dubbing duration.
Slow Down Video Playback: If simply speeding up the dubbing is ineffective, slowing down the video playback can be considered. For example, if the original audio duration for a subtitle is 1 second and the dubbed version becomes 3 seconds, the dubbing duration can be shortened to 2 seconds (by doubling the speed), while the corresponding video segment's playback speed is reduced by half (extending its duration to 2 seconds), achieving synchronization.
Each of the above methods has its pros and cons and cannot perfectly solve all problems. Achieving optimal synchronization often requires manual fine-tuning, which contradicts the goal of software automation. Therefore, video translation software typically combines these strategies to strive for the best possible outcome.
Implementation in Video Translation Software
In software, these strategies are typically controlled through the following settings:
- Main Interface Settings:
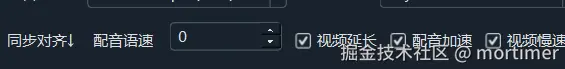
"Dubbing Speed" setting is used to globally accelerate the dubbing;
"Dubbing Acceleration" setting automatically increases dubbing duration to match subtitles;
"Video Slow Speed" setting automatically reduces video playback speed to match dubbing duration;
"Video Extension" setting freezes the last frame of the video until the dubbing ends.
Advanced Options Settings (Menu Bar → Tools/Options → Advanced Options → Subtitle-Audio-Visual Synchronization):
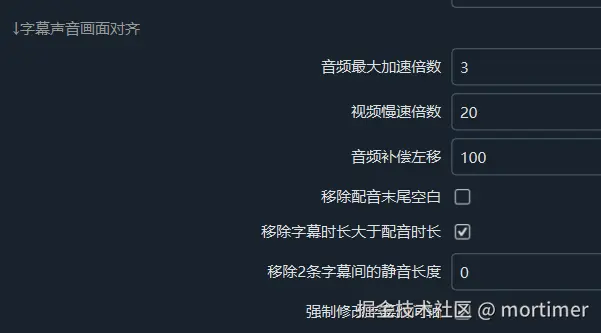
Options like "Remove Blank at End of Dubbing," "Remove Silence Between Two Subtitles," and "Remove Subtitle Duration Longer Than Dubbing Duration" allow users to finely control subtitle and dubbing synchronization.
Additionally, "Maximum Audio Acceleration Multiplier" (default 3x) and "Video Slow Speed Multiplier" (default 20x) limit the degree of acceleration and deceleration to prevent audio distortion or excessively slow video playback.Audio Compensation Left Shift:
Due to precision limitations in the underlying technology (ffmpeg), even if synchronization is achieved at the start, over time, the dubbing duration may gradually exceed the subtitle duration. The "Audio Compensation Left Shift" setting shifts the entire subtitle timeline to the left, effectively mitigating this issue, such as eliminating a gap between subtitles every 3 minutes.
By flexibly applying the above settings, video translation software can automate the synchronization of subtitles and dubbing as much as possible, improving translation efficiency.
