Hard subs, soft subs, external subs—just the names can be confusing, not to mention that some players display subtitles while others don't. If you often find yourself lost in these issues, this guide is for you. From the basic differences between subtitle types to hands-on FFmpeg operations, we'll break it down step by step—simple and practical!
I. Understanding Subtitle Types
1. Hard Subtitles (Burned-in Subtitles)


- Definition: Subtitles are directly rendered onto the video frames, becoming part of the image.
- Characteristics:
- Cannot be turned off; permanently displayed.
- High compatibility; playable on any device.
- Fixed style (font, color, etc.); cannot be adjusted.
- Use Cases:
- Anti-piracy (e.g., watermarks on streaming platforms).
- Low-end devices (e.g., older TVs) for subtitle display.
2. Soft Subtitles (Embedded Subtitles)
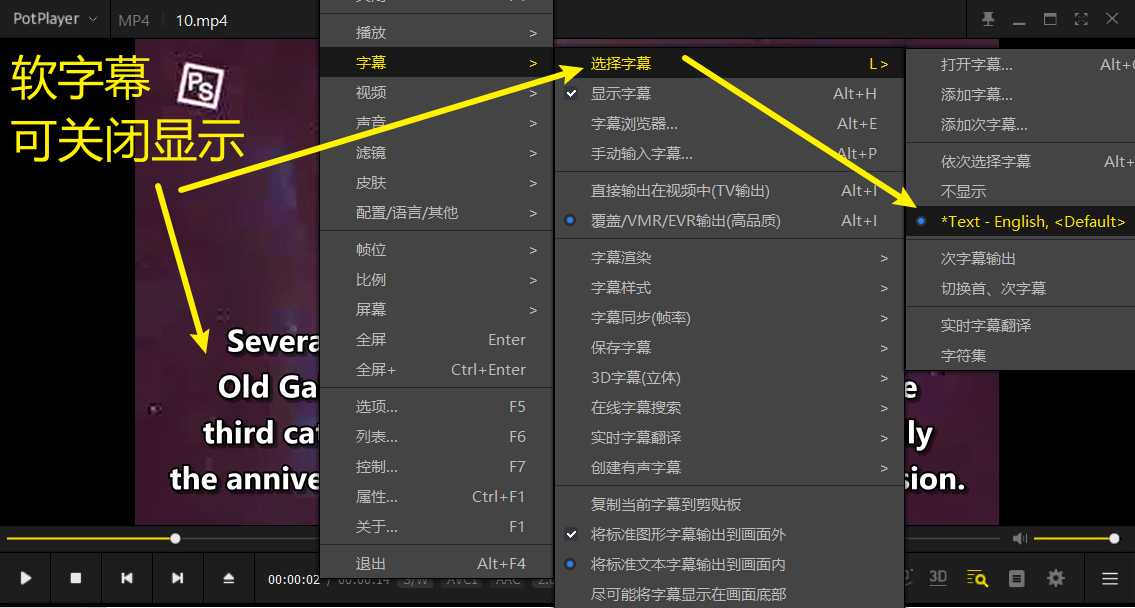

- Definition: Subtitles are stored as separate tracks within the video file (e.g.,
mov_texttrack in MP4). - Characteristics:
- Can be toggled on/off or switched between languages.
- Requires player support (some devices may not recognize them).
- Style can be customized by the player.
- Use Cases:
- Multi-language videos (e.g., switching between Chinese and English subtitles in movies).
- Streaming distribution (e.g., Netflix).
3. External Subtitles
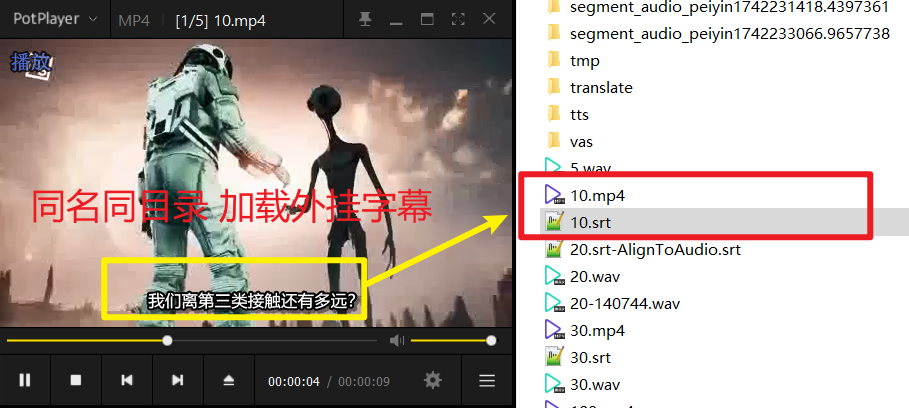
- Definition: Separate subtitle files (e.g.,
.srt,.ass) that need to be loaded manually. - Characteristics:
- Flexible editing without affecting the original video.
- Usually stored with the same name as the video (e.g.,
video.mp4+video.srt). - Dependent on player support.
- Use Cases:
- Temporary use or frequent subtitle adjustments.
II. Comparing Main Subtitle Formats: SRT vs ASS
| Feature | SRT | ASS |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | Plain text (timeline + text) | Supports effects (color, animation, position) |
| Style Control | Relies on player defaults | Customizable font, size, color, etc. |
| Compatibility | Almost universal support | Requires ASS-compatible players (e.g., VLC) |
| File Size | Very small | Slightly larger (includes style code) |
| Use Cases | Basic subtitles, multi-language support | Stylized subtitles, complex formatting needs |
SRT Subtitle Format Requirements
- Basic components:
- Index: Number for each subtitle segment, starting from 1 and incrementing.
- Timeline: Start and end times in the format: hours:minutes:seconds,milliseconds --> hours:minutes:seconds,milliseconds.
- Subtitle content: Plain text, supports line breaks, separated by a blank line after each segment.
- Requirements:
- File encoding recommended as UTF-8 (to avoid garbled text).
- Timeline must be precise, with three digits for milliseconds after the comma.
- No style control; entirely dependent on player rendering.
1
00:00:01,000 --> 00:00:03,500
Hello, welcome to SRT subtitles!
2
00:00:04,000 --> 00:00:06,000
This is the second subtitle segment.ASS Subtitle Format Requirements
- Basic components:
- Header info: Defines subtitle styles and metadata (e.g., resolution, font).
- Events section: Contains timeline and specific subtitle content, supports effects.
- Requirements:
- File starts with [Script Info] for global settings.
- [V4+ Styles] defines styles (e.g., font, color).
- [Events] lists the time and content for each subtitle segment.
- Supports complex effects (e.g., position, animation) using specific tags.
[Script Info]
Title: Example ASS Subtitle
ScriptType: v4.00+
PlayResX: 1280
PlayResY: 720
[V4+ Styles]
Format: Name, Fontname, Fontsize, PrimaryColour, Alignment
Style: Default, Microsoft YaHei, 36, &H00FFFFFF, 2
[Events]
Format: Layer, Start, End, Style, Text
Dialogue: 0, 0:00:01.00, 0:00:03.50, Default, Hello, welcome to ASS subtitles!
Dialogue: 0, 0:00:04.00, 0:00:06.00, Default, {\pos(640,360)}This is the second centered subtitle.III. How to Choose a Subtitle Embedding Method?
1. Based on Needs
- Hard Subtitles: For mandatory display (e.g., promotional videos) or when target devices don't support soft subtitles.
- Soft Subtitles: When flexibility to toggle on/off is needed (e.g., multi-language videos) and original video quality should be preserved.
- External Subtitles: For temporary use or frequent subtitle content changes.
2. Based on Format
- SRT: For basic text only, no special effects needed, suitable for cross-platform distribution.
- ASS: When font, size, color, and other effects are required, and users have ASS-compatible players.
IV. FFmpeg Practical Operations
1. Embed Hard Subtitles (Preserving ASS Effects)
bash
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -vf "ass=subtitle.ass" -c:a copy output.mp4- Explanation: Renders ASS subtitles onto the video, preserving effects; audio stream is copied directly for efficiency.
2. Embed Soft Subtitles (SRT or ASS)
bash
# Embed SRT
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -i subtitle.srt -c:v copy -c:a copy -c:s mov_text -metadata:s:s:0 language=chi output.mp4
# Embed ASS (effects may be lost)
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -i subtitle.ass -c:v copy -c:a copy -c:s mov_text output.mp4- Note: MP4's
mov_textdoesn't support ASS effects; consider using MKV instead.
3. Force Hard Subtitle Styles (Overriding Original ASS Settings)
bash
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -vf "subtitles=subtitle.ass:force_style='FontName=Microsoft YaHei,FontSize=24,PrimaryColour=&H00FFFFFF'" -c:a copy output.mp4- Parameter Explanation:
FontName: Font name (must be supported by the system).FontSize: Font size.PrimaryColour: Color (&HBBGGRRAA, e.g.,&H00FFFFFFfor white).
V. Frequently Asked Questions
1. Do soft and external subtitles display simultaneously after embedding?
- Usually not: Players (e.g., VLC) prioritize external subtitles; you can manually switch tracks.
- If overlapping: Disable one track in the player settings.
2. How to embed multiple language subtitles?
bash
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -i chs.srt -i eng.srt -c:v copy -c:a copy -c:s mov_text -metadata:s:s:0 language=chi -metadata:s:s:1 language=eng output.mp4- Usage: Switch language tracks via the player menu.
3. What if ASS effects don't work in MP4?
- Reason: MP4's
mov_textdoesn't support complex ASS effects. - Solutions:
- Use MKV container (supports native ASS embedding):bash
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -i subtitle.ass -c:v copy -c:a copy -c:s copy output.mkv - Convert to hard subtitles (preserves effects but loses flexibility).
- Use MKV container (supports native ASS embedding):
VI. Final Selection Recommendations
| Scenario | Recommended Solution |
|---|---|
| Simple subtitles, high compatibility | SRT soft or hard subtitles |
| Stylized subtitles, local playback | ASS hard subtitles or MKV soft subtitles |
| Multi-language needs | Multi-track SRT soft subtitles |
| Uploading to streaming platforms | SRT soft subtitles (platform-optimized) |
VII. Other Useful Tips
Check Subtitle Encoding
- If subtitles show garbled text, check file encoding (recommended: UTF-8). Use tools like Notepad++ for conversion.
Adjust Timeline
- Use FFmpeg to adjust subtitle delay:bash
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -vf "subtitles=subtitle.srt:si=0:setpts=PTS-STARTPTS+0.5/TB" output.mp40.5means a 0.5-second delay; adjust as needed.
- Use FFmpeg to adjust subtitle delay:
