Everyone knows that Microsoft Edge has a powerful text-to-speech feature that supports dozens of languages, each with different voice options for pronunciation, delivering excellent results.
Based on this, developers have created a Python package called edge-tts. This package allows the use of Microsoft's TTS service in programs for dubbing text or subtitles. For example, the video translation software pyVideoTrans integrates edge-tts, enabling users to select it directly in the dubbing channel.
Unfortunately, there has been significant misuse of Microsoft TTS by users in China, including using it for commercial dubbing sales. This has led Microsoft to restrict access from China. If used too frequently, you may encounter a 403 error, and only switching IPs or connecting to a stable VPN outside China can restore access.
So, is it possible to set up a simple relay service on a foreign server for personal use? This approach can improve stability and make the interface compatible with OpenAI TTS, allowing direct use in the OpenAI SDK.
The answer is yes. I recently took the time to create a Docker image that can be easily pulled and started on a server.
Once started, the service interface is fully compatible with OpenAI. Simply change the API address to http://your-server-ip:7899/v1 to seamlessly replace OpenAI TTS. Additionally, it can be used directly in video translation software.
The following details how to deploy and use it:
Step 1: Purchase and activate a US server
Step 2: Open port 7899 in the firewall
Step 3: Connect to the server via terminal
Step 4: Install Docker
Step 5: Pull the edge-tts-api image and start the API service
If you already have a server with Docker installed, skip to Step 5 to pull the image.
Step 1: Purchase and Activate a US Server
It is recommended to choose a server in the US region due to fewer or no restrictions. The server OS can be a Linux distribution; the following uses Debian 12 as an example, with Yecaoyun as the provider. The reason for choosing it is simple: it's cheap and relatively stable, sufficient for a dubbing relay.
If you already have a Linux server in Europe or the US, you can skip this section and proceed to the next. If not, continue reading.
Then, choose any of the top four configurations; any should be sufficient.
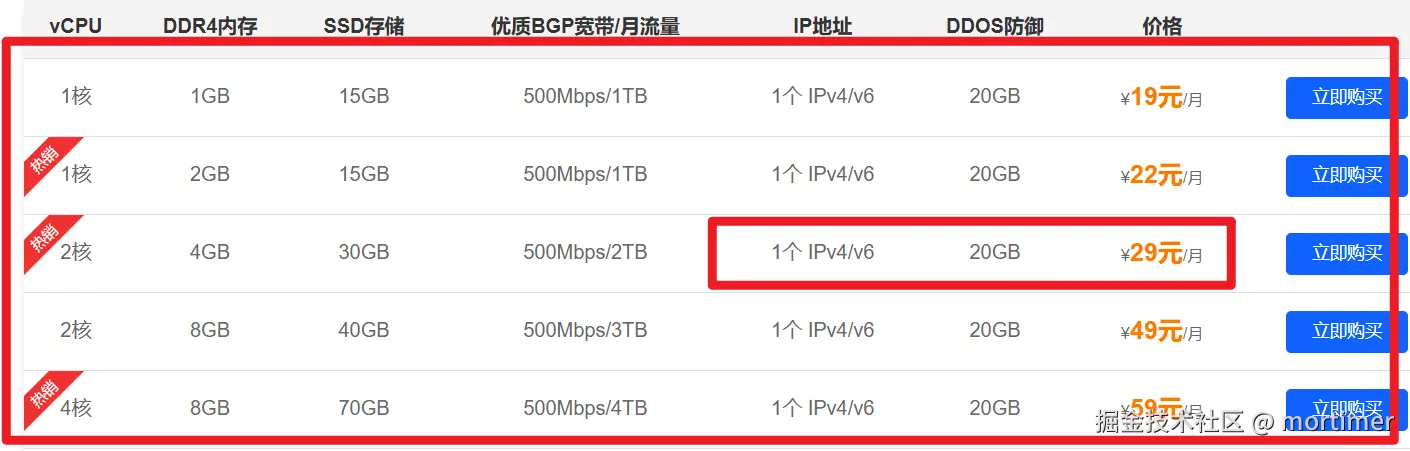
I personally use the 29 RMB/month configuration.
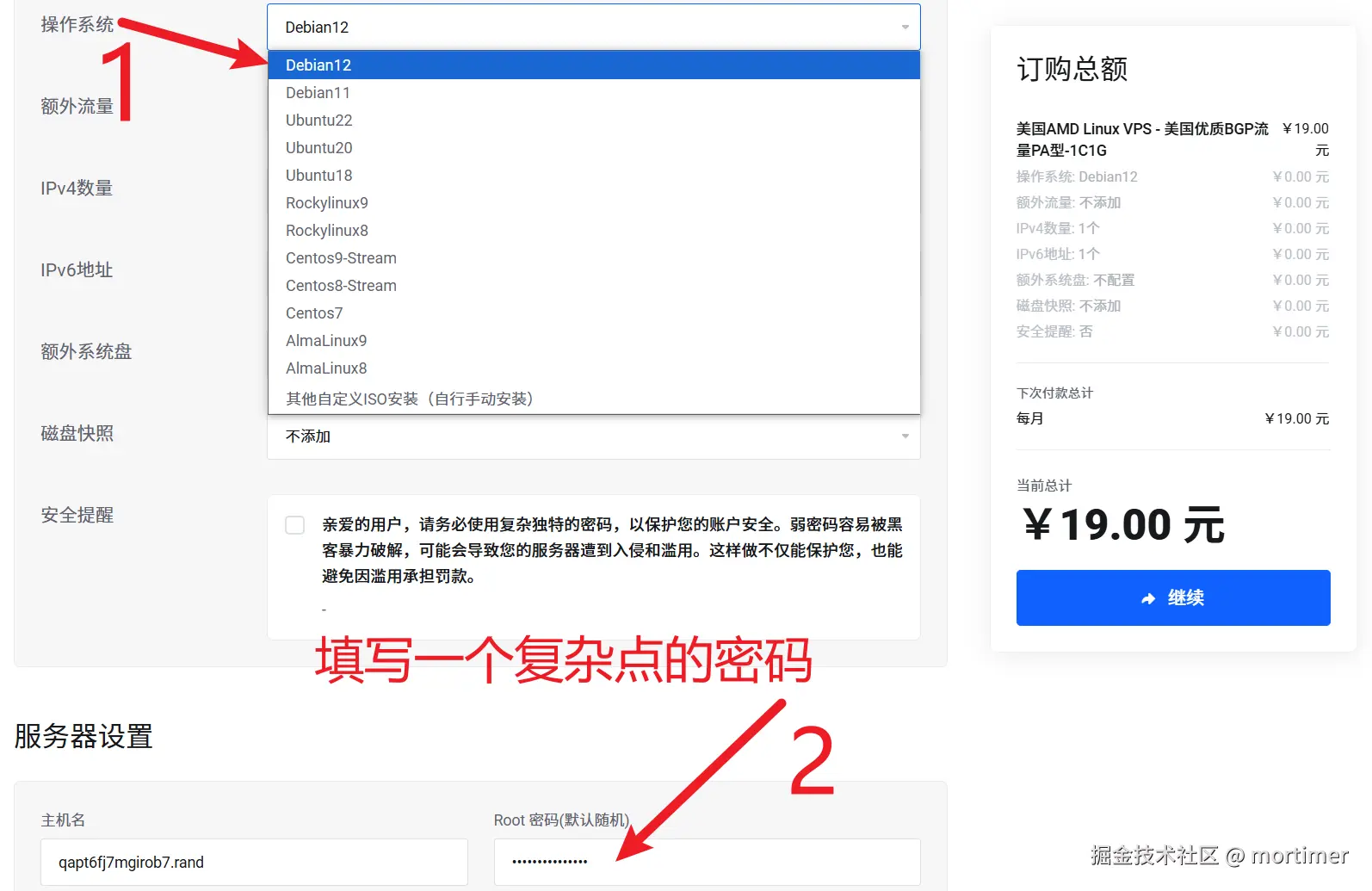
Click the "Buy Now" button to go to the configuration page. Here, select the server OS as Debian 12, set the server password, and keep the rest as default.
After payment, wait a few minutes for the server to be created and started. Next, you need to configure the firewall to open port 7899. Only by opening this port can you connect to the service for dubbing.
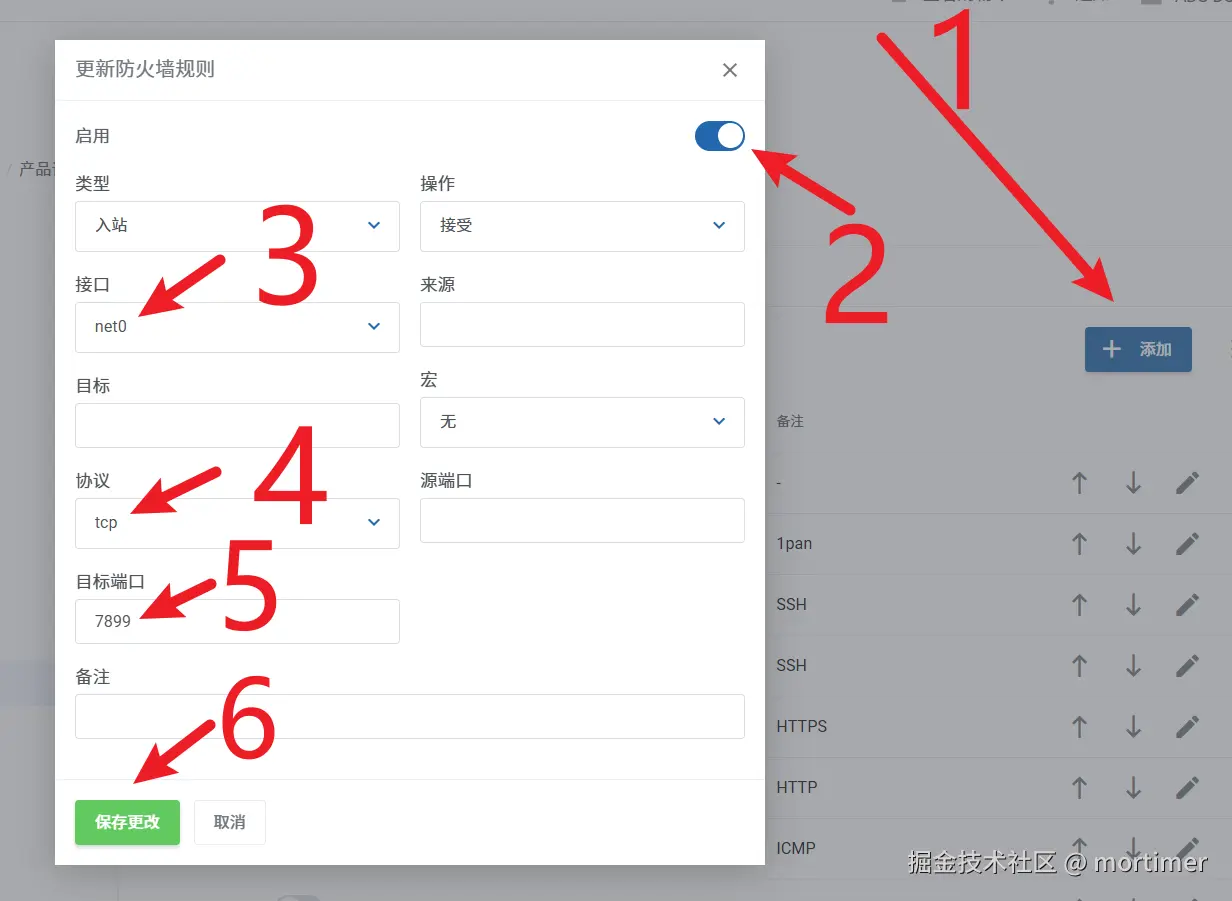
Step 2: Open Port 7899 in the Firewall
If you plan to use a domain name and configure Nginx reverse proxy, you don't need to open the port. If you're not familiar with these, for simplicity, it's recommended to open the port directly.
Firewall settings vary across different servers and panels. The following uses Yecaoyun's panel as an example; other panels can be referenced similarly. If you know how to open a port, skip this section and proceed to the next.
First, in "My Products & Services," click on the product you just activated to enter the product information and management page.
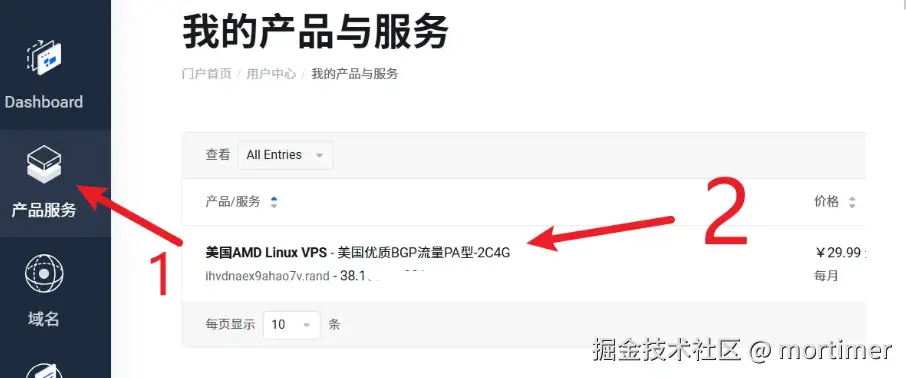
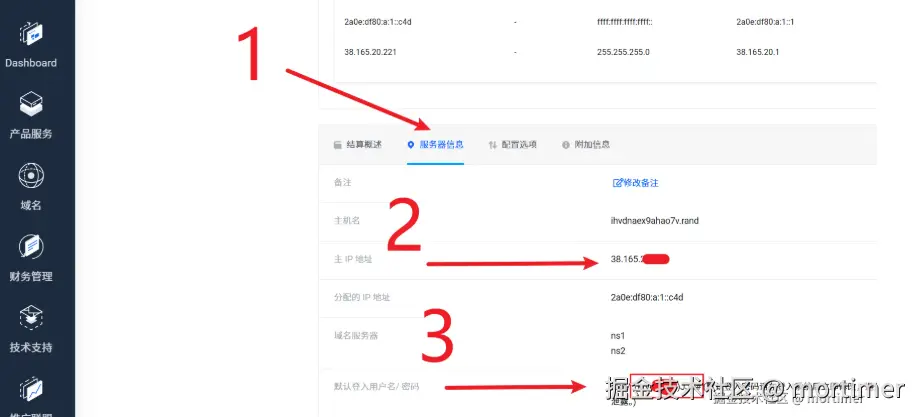
On this page, you can find the server's IP address, password, and other information.
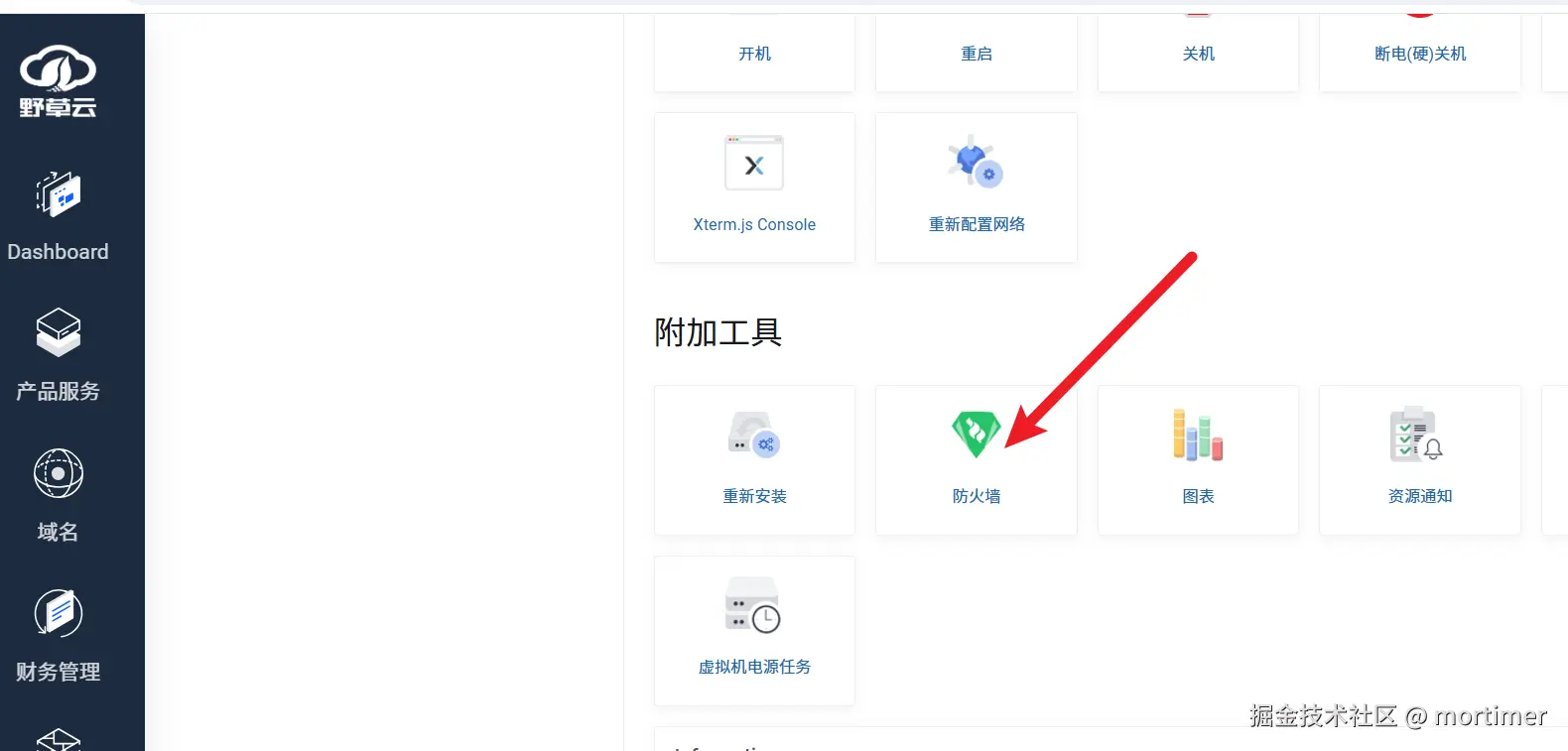
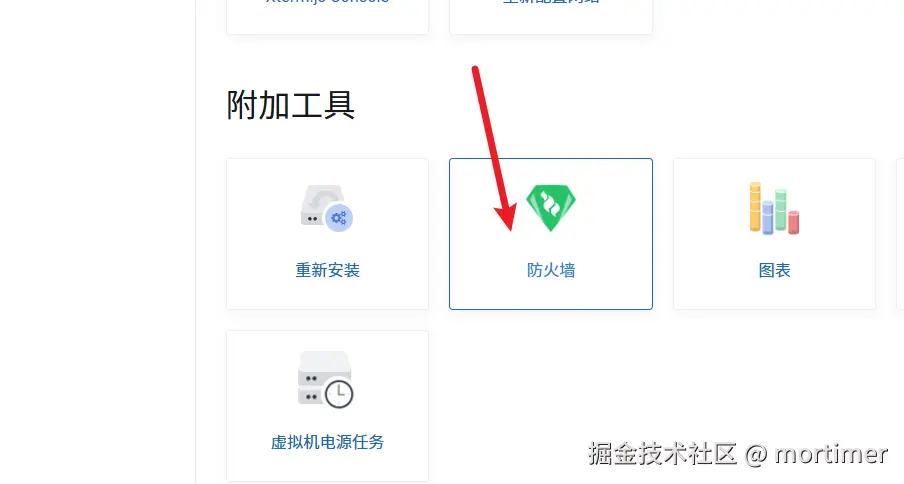
Find "Firewall" under "Additional Tools" and click to open it.
Then open port 7899 as shown below:
Step 3: Connect to the Server via Terminal
If you already know how to connect via terminal or have other SSH terminals like Xshell, skip this step and proceed to the next section.
On the product information page, find Xterm.js Console and click it. Then follow the steps below:
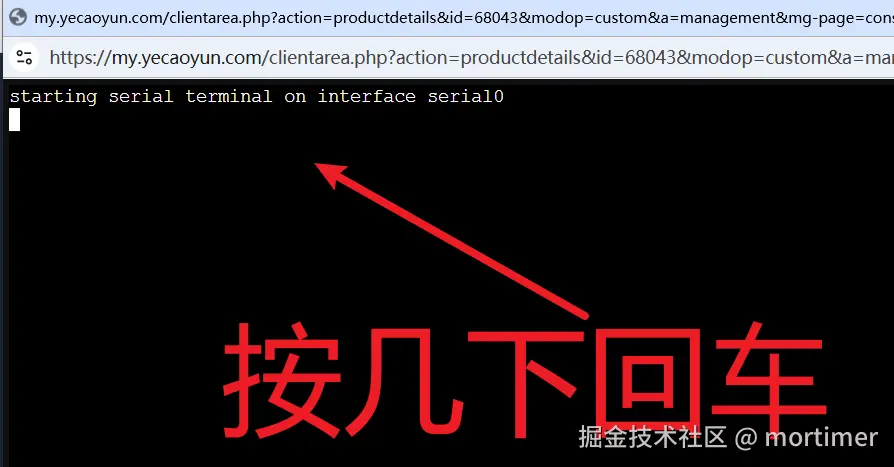
When the above appears, press Enter a few times.
When Login: appears, type root after it and press Enter. 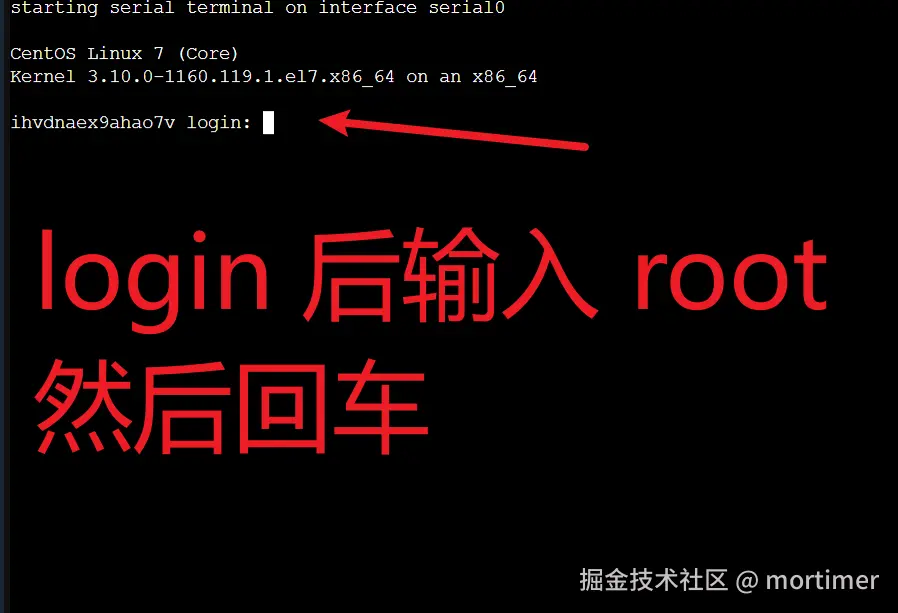
Then Password: will appear. Paste the password you copied (if forgotten, you can find it on the product information page).
Note: Do not use Ctrl+V or right-click to paste, as this may add extra spaces or line breaks, causing password errors.
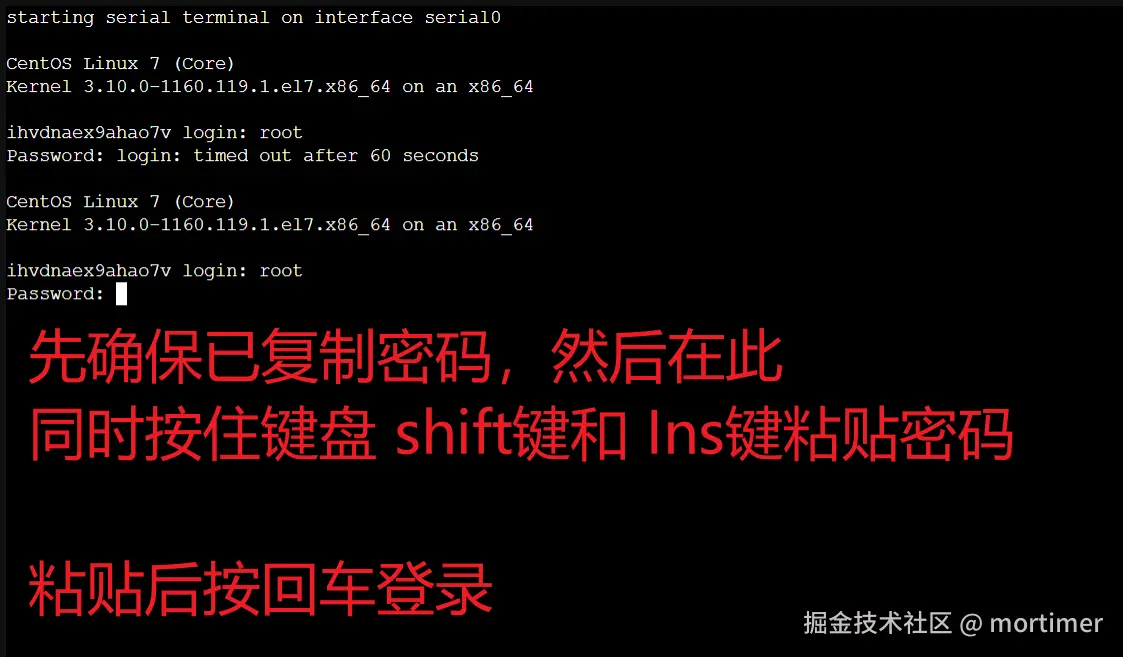
Hold Shift + Insert to paste the password to avoid login issues, then press Enter.

After successful login, it will look like the image below.

Step 4: Install Docker
If Docker is already installed on your server or you know how to install it, skip this step.
Execute the following 5 commands in order, ensuring each command completes successfully before running the next. These commands are for Debian 12 series servers.
After [root@xxxxxx~]#, right-click to paste the command, then press Enter to execute.
Command 1: sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg
Command 2: curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/debian/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg
Command 3: echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/debian $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
Command 4: sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin
Command 5: Start Docker service. sudo systemctl start docker && sudo systemctl enable docker && sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
You can right-click to paste this command, then press Enter.
Step 5: Pull the edge-tts-api Image and Start the API Service
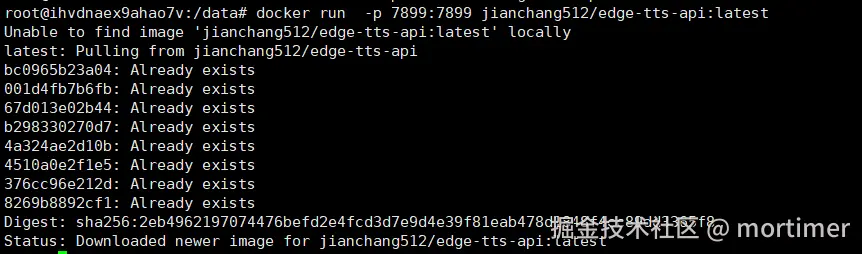
Enter the following command to automatically pull the image and start the service. Once started successfully, you can use it in video translation software or other tools that support OpenAI TTS.
docker run -p 7899:7899 jianchang512/edge-tts-api:latest

Press Ctrl+C repeatedly to stop the service.
Note: This command runs in the foreground. If you close the terminal window, the service will stop.
You can use the following command instead to start the service in the background, allowing you to safely close the terminal after execution.
docker run -d -p 7899:7899 jianchang512/edge-tts-api:latest
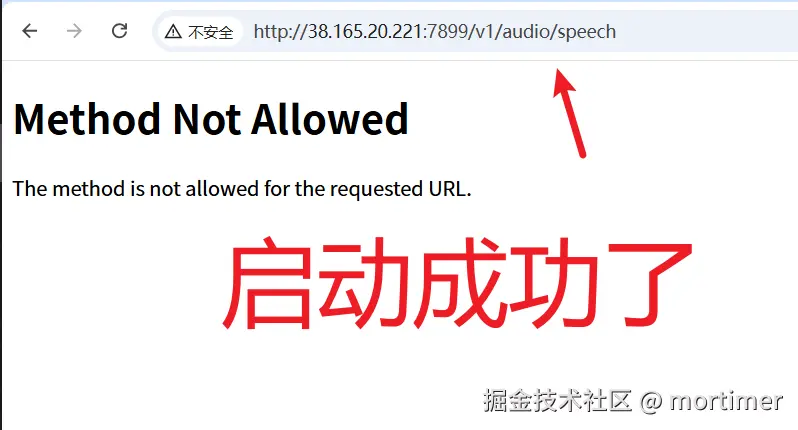
If there are no errors, the service has started successfully. You can verify by opening http://your-ip:7899/v1/audio/speech in a browser. If you see a result similar to the image below, it means the service is running.
Using in Video Translation Software
Please upgrade the software to v3.40 to use this feature. Download the upgrade from https://pyvideotrans.com/downpackage.
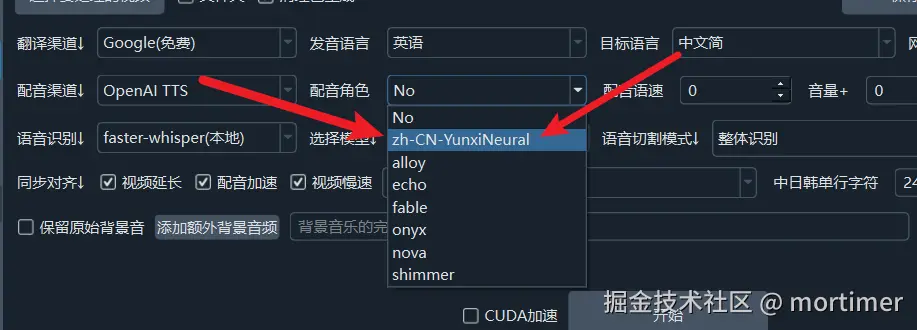
Open the menu, go to TTS Settings -> OpenAI TTS, and change the interface address to http://your-ip:7899/v1.
SK can be filled arbitrarily, as long as it's not empty. In the voice list, enter the voices you want to use, separated by English commas.
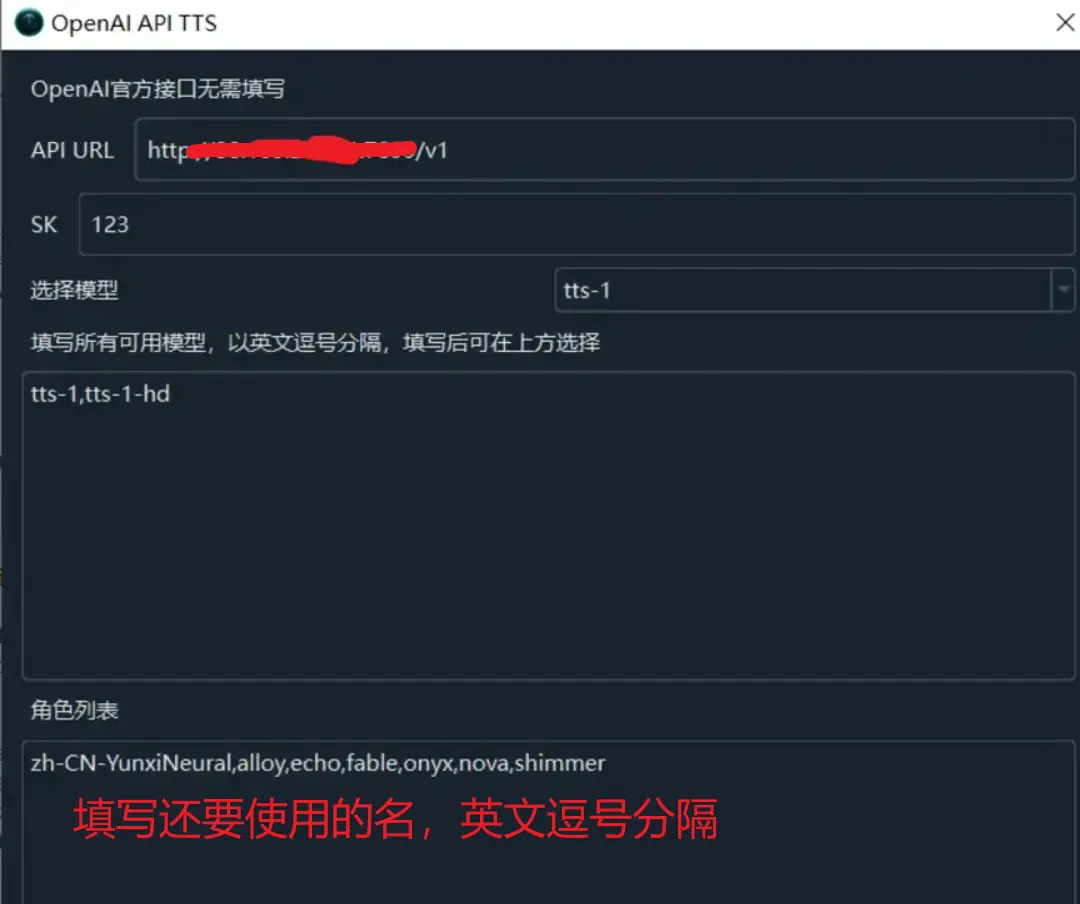
Available Voices
Below is the list of available voices. Note that the text language and voice must match.
Chinese Voices:
zh-HK-HiuGaaiNeural
zh-HK-HiuMaanNeural
zh-HK-WanLungNeural
zh-CN-XiaoxiaoNeural
zh-CN-XiaoyiNeural
zh-CN-YunjianNeural
zh-CN-YunxiNeural
zh-CN-YunxiaNeural
zh-CN-YunyangNeural
zh-CN-liaoning-XiaobeiNeural
zh-TW-HsiaoChenNeural
zh-TW-YunJheNeural
zh-TW-HsiaoYuNeural
zh-CN-shaanxi-XiaoniNeural
English Voices:
en-AU-NatashaNeural
en-AU-WilliamNeural
en-CA-ClaraNeural
en-CA-LiamNeural
en-HK-SamNeural
en-HK-YanNeural
en-IN-NeerjaExpressiveNeural
en-IN-NeerjaNeural
en-IN-PrabhatNeural
en-IE-ConnorNeural
en-IE-EmilyNeural
en-KE-AsiliaNeural
en-KE-ChilembaNeural
en-NZ-MitchellNeural
en-NZ-MollyNeural
en-NG-AbeoNeural
en-NG-EzinneNeural
en-PH-JamesNeural
en-PH-RosaNeural
en-SG-LunaNeural
en-SG-WayneNeural
en-ZA-LeahNeural
en-ZA-LukeNeural
en-TZ-ElimuNeural
en-TZ-ImaniNeural
en-GB-LibbyNeural
en-GB-MaisieNeural
en-GB-RyanNeural
en-GB-SoniaNeural
en-GB-ThomasNeural
en-US-AvaMultilingualNeural
en-US-AndrewMultilingualNeural
en-US-EmmaMultilingualNeural
en-US-BrianMultilingualNeural
en-US-AvaNeural
en-US-AndrewNeural
en-US-EmmaNeural
en-US-BrianNeural
en-US-AnaNeural
en-US-AriaNeural
en-US-ChristopherNeural
en-US-EricNeural
en-US-GuyNeural
en-US-JennyNeural
en-US-MichelleNeural
en-US-RogerNeural
en-US-SteffanNeural
Japanese Voices:
ja-JP-KeitaNeural
ja-JP-NanamiNeural
Korean Voices:
ko-KR-HyunsuNeural
ko-KR-InJoonNeural
ko-KR-SunHiNeural
French Voices:
fr-BE-CharlineNeural
fr-BE-GerardNeural
fr-CA-ThierryNeural
fr-CA-AntoineNeural
fr-CA-JeanNeural
fr-CA-SylvieNeural
fr-FR-VivienneMultilingualNeural
fr-FR-RemyMultilingualNeural
fr-FR-DeniseNeural
fr-FR-EloiseNeural
fr-FR-HenriNeural
fr-CH-ArianeNeural
fr-CH-FabriceNeural
German Voices:
de-AT-IngridNeural
de-AT-JonasNeural
de-DE-SeraphinaMultilingualNeural
de-DE-FlorianMultilingualNeural
de-DE-AmalaNeural
de-DE-ConradNeural
de-DE-KatjaNeural
de-DE-KillianNeural
de-CH-JanNeural
de-CH-LeniNeural
Spanish Voices:
es-AR-ElenaNeural
es-AR-TomasNeural
es-BO-MarceloNeural
es-BO-SofiaNeural
es-CL-CatalinaNeural
es-CL-LorenzoNeural
es-ES-XimenaNeural
es-CO-GonzaloNeural
es-CO-SalomeNeural
es-CR-JuanNeural
es-CR-MariaNeural
es-CU-BelkysNeural
es-CU-ManuelNeural
es-DO-EmilioNeural
es-DO-RamonaNeural
es-EC-AndreaNeural
es-EC-LuisNeural
es-SV-LorenaNeural
es-SV-RodrigoNeural
es-GQ-JavierNeural
es-GQ-TeresaNeural
es-GT-AndresNeural
es-GT-MartaNeural
es-HN-CarlosNeural
es-HN-KarlaNeural
es-MX-DaliaNeural
es-MX-JorgeNeural
es-NI-FedericoNeural
es-NI-YolandaNeural
es-PA-MargaritaNeural
es-PA-RobertoNeural
es-PY-MarioNeural
es-PY-TaniaNeural
es-PE-AlexNeural
es-PE-CamilaNeural
es-PR-KarinaNeural
es-PR-VictorNeural
es-ES-AlvaroNeural
es-ES-ElviraNeural
es-US-AlonsoNeural
es-US-PalomaNeural
es-UY-MateoNeural
es-UY-ValentinaNeural
es-VE-PaolaNeural
es-VE-SebastianNeural
Arabic Voices:
ar-DZ-AminaNeural
ar-DZ-IsmaelNeural
ar-BH-AliNeural
ar-BH-LailaNeural
ar-EG-SalmaNeural
ar-EG-ShakirNeural
ar-IQ-BasselNeural
ar-IQ-RanaNeural
ar-JO-SanaNeural
ar-JO-TaimNeural
ar-KW-FahedNeural
ar-KW-NouraNeural
ar-LB-LaylaNeural
ar-LB-RamiNeural
ar-LY-ImanNeural
ar-LY-OmarNeural
ar-MA-JamalNeural
ar-MA-MounaNeural
ar-OM-AbdullahNeural
ar-OM-AyshaNeural
ar-QA-AmalNeural
ar-QA-MoazNeural
ar-SA-HamedNeural
ar-SA-ZariyahNeural
ar-SY-AmanyNeural
ar-SY-LaithNeural
ar-TN-HediNeural
ar-TN-ReemNeural
ar-AE-FatimaNeural
ar-AE-HamdanNeural
ar-YE-MaryamNeural
ar-YE-SalehNeural
Bengali Voices:
bn-BD-NabanitaNeural
bn-BD-PradeepNeural
bn-IN-BashkarNeural
bn-IN-TanishaaNeural
Czech Voices:
cs-CZ-AntoninNeural
cs-CZ-VlastaNeural
Dutch Voices:
nl-BE-ArnaudNeural
nl-BE-DenaNeural
nl-NL-ColetteNeural
nl-NL-FennaNeural
nl-NL-MaartenNeural
Hebrew Voices:
he-IL-AvriNeural
he-IL-HilaNeural
Hindi Voices:
hi-IN-MadhurNeural
hi-IN-SwaraNeural
Hungarian Voices:
hu-HU-NoemiNeural
hu-HU-TamasNeural
Indonesian Voices:
id-ID-ArdiNeural
id-ID-GadisNeural
Italian Voices:
it-IT-GiuseppeNeural
it-IT-DiegoNeural
it-IT-ElsaNeural
it-IT-IsabellaNeural
Kazakh Voices:
kk-KZ-AigulNeural
kk-KZ-DauletNeural
Malay Voices:
ms-MY-OsmanNeural
ms-MY-YasminNeural
Polish Voices:
pl-PL-MarekNeural
pl-PL-ZofiaNeural
Portuguese Voices:
pt-BR-ThalitaNeural
pt-BR-AntonioNeural
pt-BR-FranciscaNeural
pt-PT-DuarteNeural
pt-PT-RaquelNeural
Russian Voices:
ru-RU-DmitryNeural
ru-RU-SvetlanaNeural
Swahili Voices:
sw-KE-RafikiNeural
sw-KE-ZuriNeural
sw-TZ-DaudiNeural
sw-TZ-RehemaNeural
Thai Voices:
th-TH-NiwatNeural
th-TH-PremwadeeNeural
Turkish Voices:
tr-TR-AhmetNeural
tr-TR-EmelNeural
Ukrainian Voices:
uk-UA-OstapNeural
uk-UA-PolinaNeural
Vietnamese Voices:
vi-VN-HoaiMyNeural
vi-VN-NamMinhNeuralUsing in OpenAI SDK
Install the openai library: pip install openai
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(api_key='12314', base_url='http://your-ip:7899/v1')
with client.audio.speech.with_streaming_response.create(
model='tts-1',
voice='zh-CN-YunxiNeural',
input='Hello, dear friends',
speed=1.0
) as response:
with open('./test.mp3', 'wb') as f:
for chunk in response.iter_bytes():
f.write(chunk)Directly Using requests to Call
import requests
res = requests.post('http://your-ip:7899/v1', data={"voice": "zh-CN-YunxiNeural",
"input": "Hello, dear friends",
"speed": 1.0})
with open('./test.mp3', 'wb') as f:
f.write(res.content)