如果你不需要CUDA加速,则无需安装和配置CUDA、cuDNN等
CUDA 是英伟达(NVIDIA)推出的一种工具,能让你的显卡帮你干更多活儿。在本软件(pyVideoTrans)中,如果想启用CUDA加速,必须先安装CUDA环境,本文将手把手教你在 Windows 10 上安装 CUDA 12.8,以及配套的 cuDNN 9.11。
Windows预打包版绑定的是 CUDA12.8,其他版本未测试 Windows10上可以安装 cuDNN 9.8, Windows11必须安装cuDNN9.11或更高版本
第一步:检查你的显卡是不是英伟达的
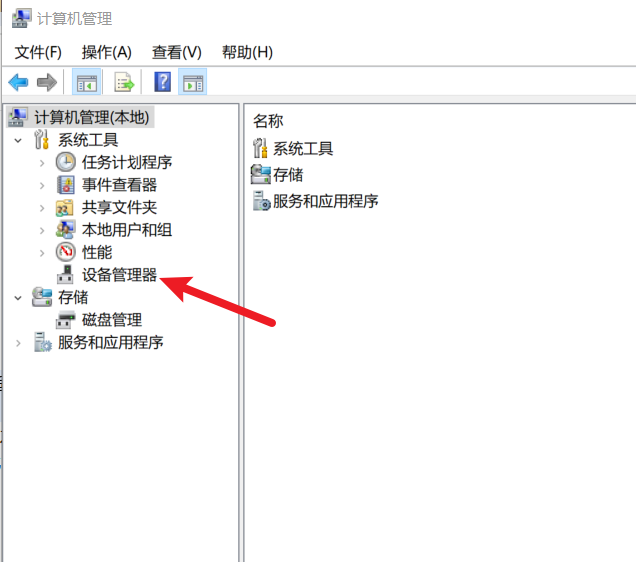
打开设备管理器
- 右键点击桌面左下角的“开始”按钮(那个 Windows 图标)。
- 在弹出的菜单里选“Windows管理工具-计算机管理”,会打开窗口。
找到显卡信息
在计算机管理打开的窗口里左侧点击
设备管理器,右侧找到“显示适配器”(Display adapters),点一下前面的小箭头展开。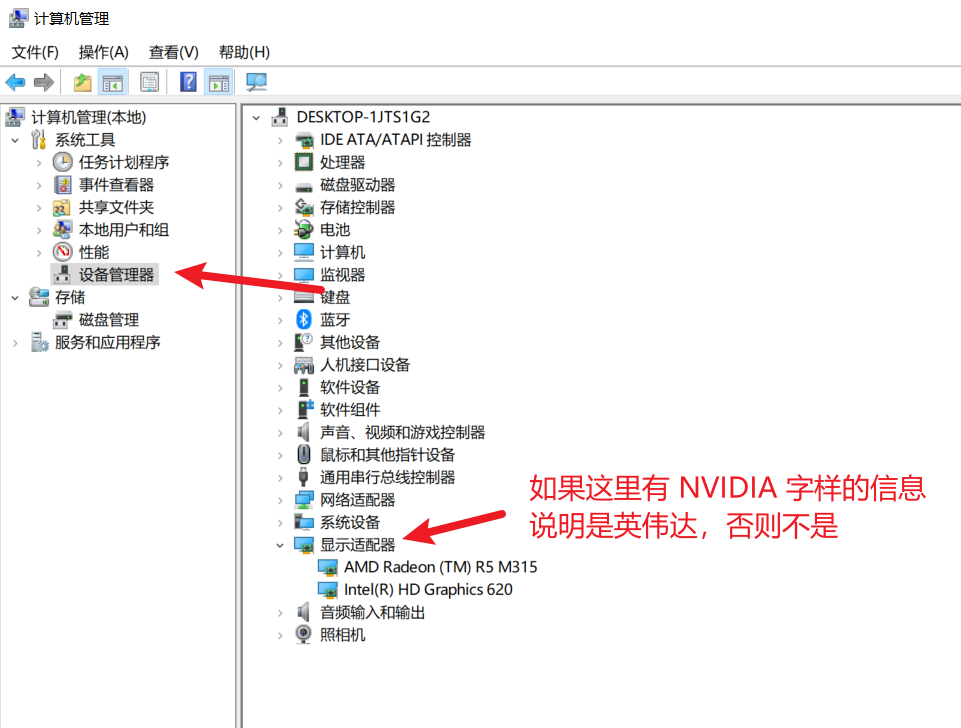
看看里面有没有“NVIDIA”字样,比如“NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1660”之类。
如果有,恭喜,你的显卡是英伟达的,可以继续往下走。如果没有(比如显示“Intel”或“AMD”),那 CUDA 用不了,教程到此为止。
第二步:检查显卡驱动版本并升级
打开英伟达管理软件
如果你装过显卡驱动,桌面右下角的任务栏(时间旁边)可能有个绿色“NVIDIA”图标。右键它,选择“NVIDIA GeForce Experience”打开。
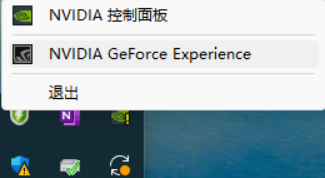
如果没有,跳到第 3 步手动下载。
检查驱动版本并升级
- 打开后,点击左上角的“驱动程序”(Drivers)。
- 它会显示当前驱动版本(比如“546.33”),如果有新版本,会有“下载”按钮。
- 点击“下载”,然后按提示安装,安装完重启电脑。
没有软件?手动下载驱动
- 打开浏览器,输入网址:https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/geforce/drivers/ 下载驱动升级软件,然后安装
- 安装后打开,按说明检查更新驱动。
第三步:检查是否已有 CUDA 并确定最大支持版本
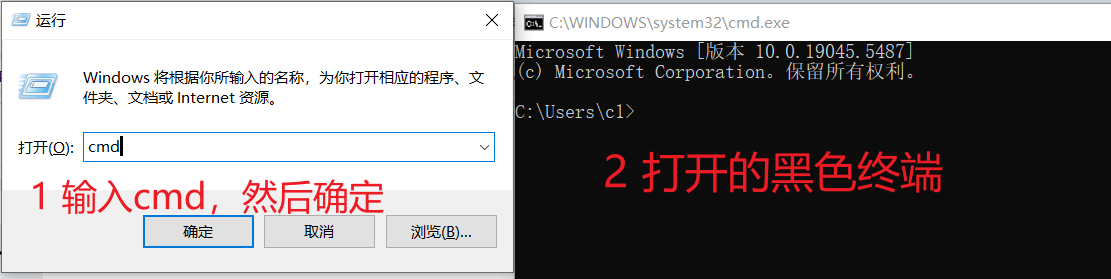
- 打开命令行终端(CMD)
- 按住键盘上的 Windows 键 + R,弹出“运行”窗口。
- 输入
cmd,按回车,打开一个黑色命令行窗口。
- 检查 CUDA 版本
- 在命令行里输入:
nvcc -V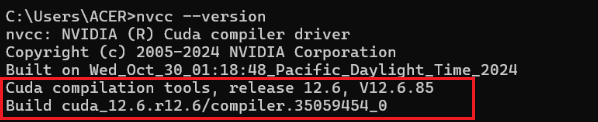
- 在命令行里输入:
按回车。如果显示类似 Cuda compilation tools, release 12.8, V12.8.xxx,说明已经装了 CUDA,版本是 12.8。如果显示“不是内部或外部命令”,说明没装过,往下走安装。
如果版本是 11.x,请先卸载然后重新安装12.8。
- 查看支持的最大 CUDA 版本
- 在命令行输入:
nvidia-smi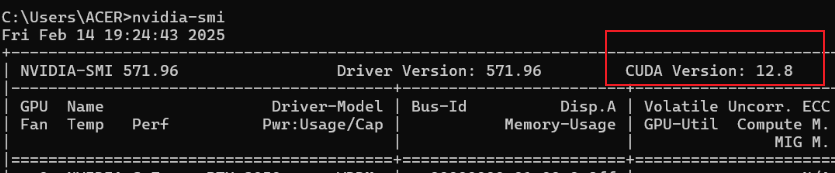
- 在命令行输入:
按回车,会显示一个表格,右上角有“CUDA Version”(比如 12.8 或更高)。这表示你的驱动支持的最高版本。只要是 12.8 或以上,就可以装我们想要的 CUDA 12.8。 如果显示是 11.x,说明显卡驱动太旧了,请先更新显卡驱动。
第四步:下载并安装 CUDA 12.8
- 下载 CUDA 12.8
- 打开浏览器,进入英伟达官网下载页面:https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-12-8-1-download-archive
- 选择“Windows” > “x86_64” > “10(如果是win11系统,则选择11)” > “exe (local)”,点击“Download”。
- 文件名大概是
cuda_12.8.1_572.61_windows.exe,会下载到你的“下载”文件夹。
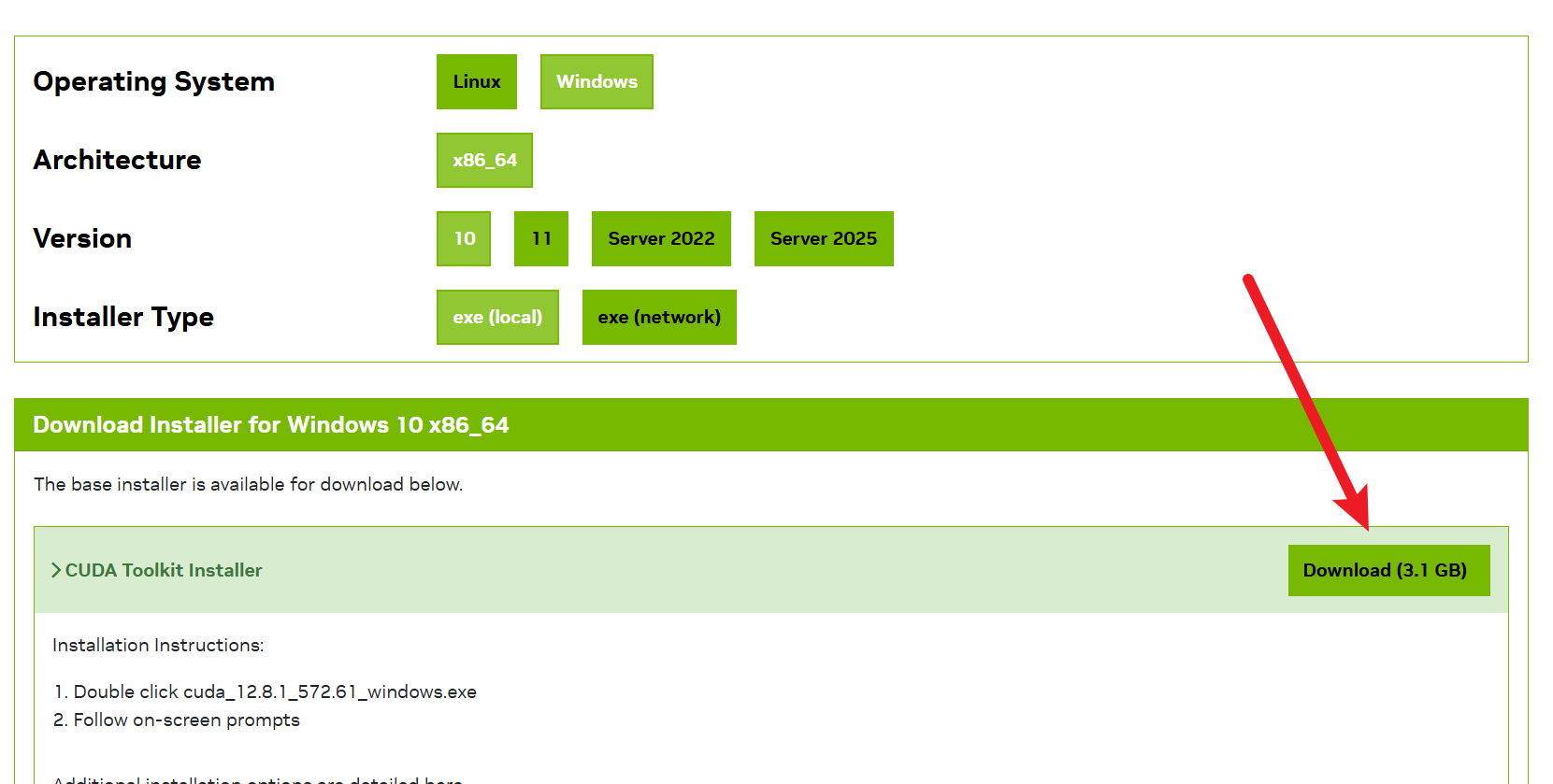
- 安装 CUDA(自定义模式)
双击下载的文件,弹出安装窗口,同意协议并下一步。
选择“自定义(高级)”安装,点击“下一步”。
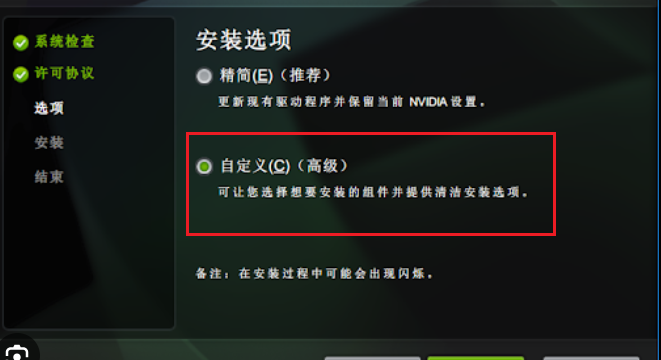
在选项列表里,只勾选第一行的“CUDA”,其他都去掉勾选,避免冲突。
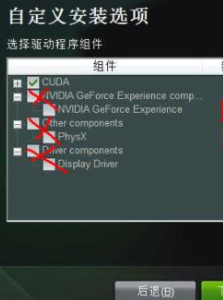
然后点击
CUDA前的+号,去掉Visual Studio Integration,否则容易安装失败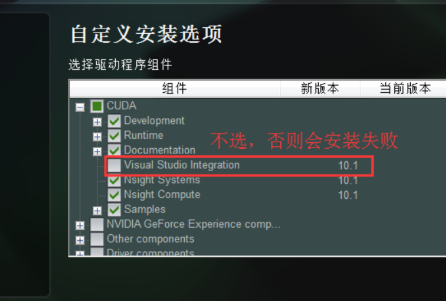
点击“下一步”,按提示完成安装,默认路径是
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v12.6。
遇到错误怎么办?
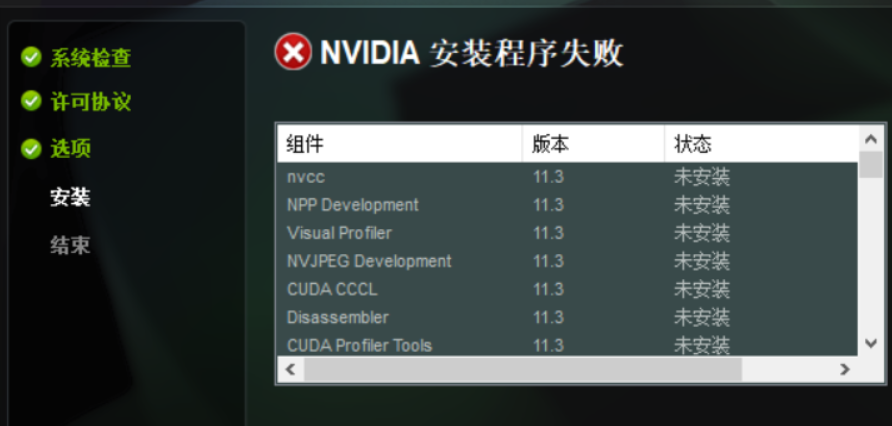
- 如果安装中断,提示“未安装”或“失败”,可能是选项没选对。重新运行安装程序,选择自定义安装,确保只选第一行的CUDA”,其他全取消,并且点开 CUDA 取消
Visual Studio Integration。 - 如果还是出错,跳到下一步安装 Visual Studio。
- 如果安装中断,提示“未安装”或“失败”,可能是选项没选对。重新运行安装程序,选择自定义安装,确保只选第一行的CUDA”,其他全取消,并且点开 CUDA 取消
第五步:安装 Visual Studio(如果 CUDA 安装失败未失败可跳过该步)
上一步如果取消了
Visual Studio Integration,应该不会出错,假如出错了,请照此安装 Visual Studio
下载 Visual Studio 社区版
- 打开浏览器,进入:https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/zh-hans/free-developer-offers/
- 点击“免费下载 Visual Studio Community”(社区版),下载安装器。
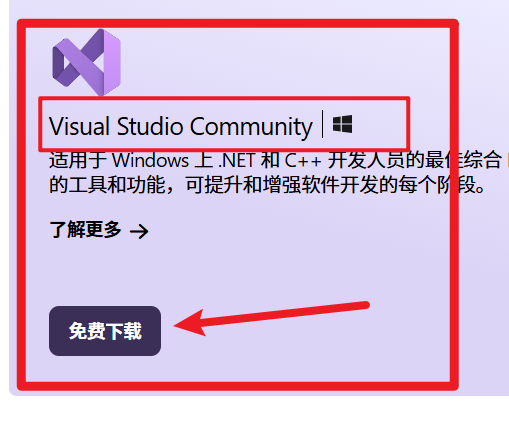
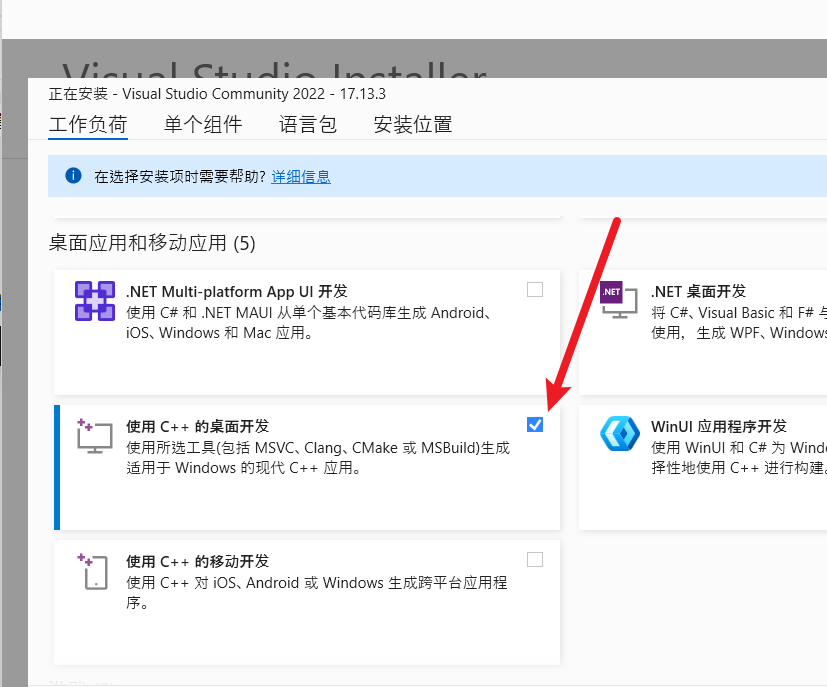
安装 C++ 开发环境
- 双击安装器,弹出窗口后选“桌面开发使用 C++”(Desktop development with C++)。
- 点击“安装”,可能需要几十分钟,装完后重启电脑。
- 重新安装 CUDA 12.8
- 回到第四步,重新运行 CUDA 安装程序,按自定义模式只选“Runtime”安装。这次应该能成功。
第六步:验证 CUDA 安装并配置环境变量
检查安装是否成功
- 打开 CMD(Windows 键 + R,输入
cmd)。 - 输入:
nvcc -V 如果显示
如果显示 Cuda compilation tools, release 12.8, V12.8.xxx,说明安装成功。如果提示“不是内部或外部命令”,需要加环境变量。
- 打开 CMD(Windows 键 + R,输入
添加 CUDA 到环境变量(默认已自动设置,如果没有,请手动添加)
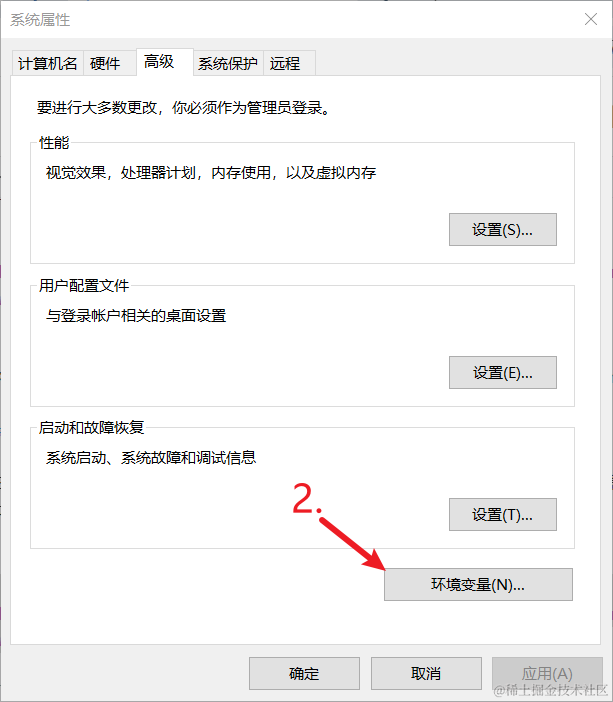
- 右键“此电脑”,选“属性” > “高级系统设置” > “环境变量”。
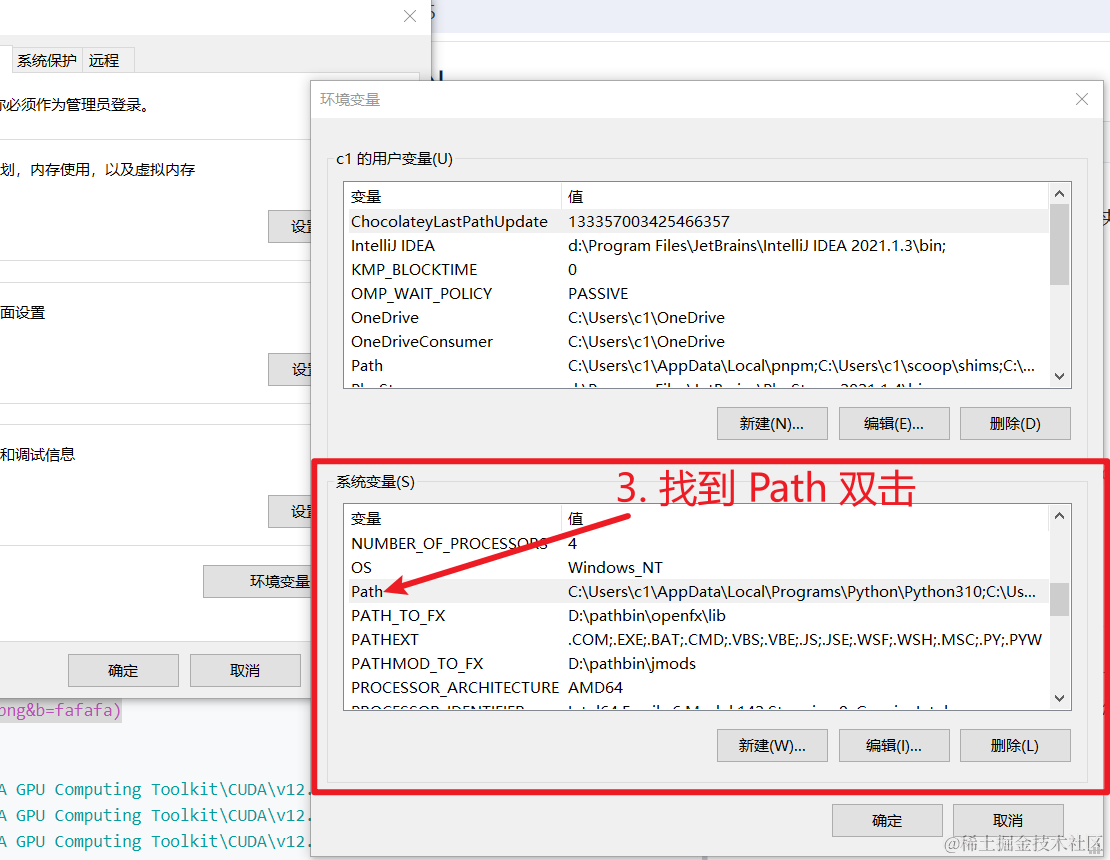
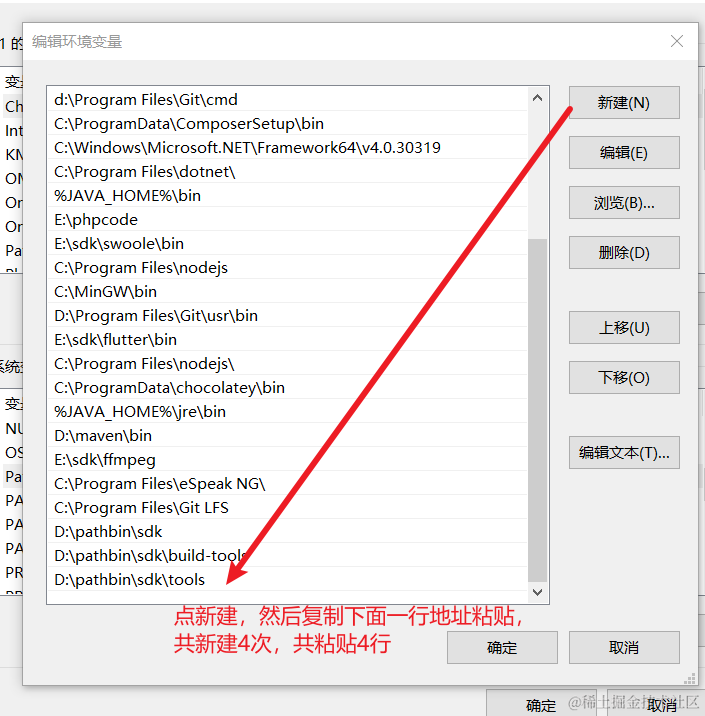
- 在“系统变量”的“Path”里,点击“新建”,输入:
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v12.8\bin C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v12.8\lib C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v12.8\include - 点击“确定”保存,关闭所有窗口。
- 重新打开 CMD,输入
nvcc -V,应该能看到版本信息了。

第七步:安装 cuDNN 9.11
- 下载 cuDNN 9.11
- 打开浏览器,进入:https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn-9-11-0-download-archive?target_os=Windows&target_arch=x86_64
- 可能需要登录英伟达账号(没有就注册一个,免费)。
- 选择“local版本”,下载 Windows 的
.exe文件
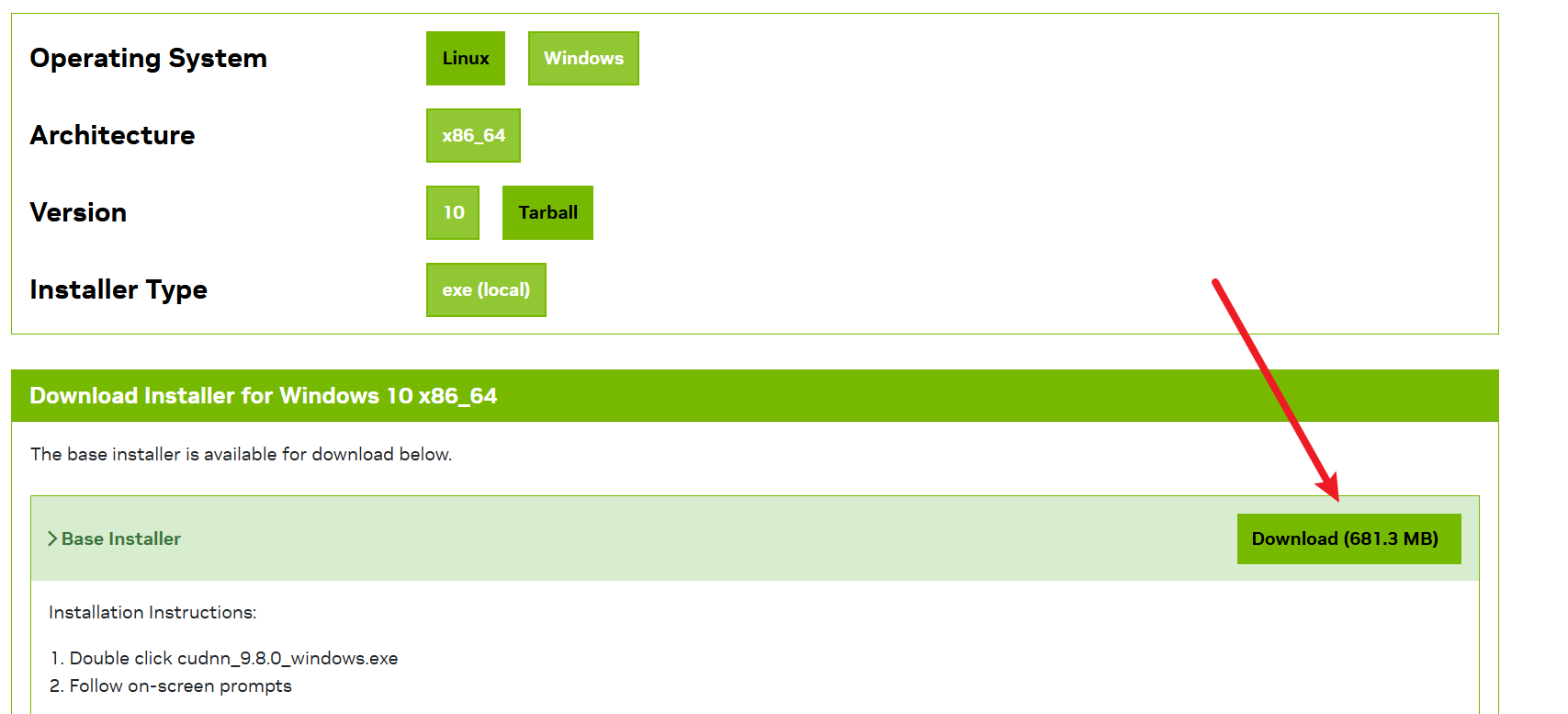
安装 cuDNN
- 双击下载的
.exe文件,按提示安装。
- 双击下载的
添加环境变量
添加方法和CUDA一样,如果你安装的不是
cudnn9.11,那么你需要修改下方的v9.11为你的版本,同时你应该进入C:\Program Files\NVIDIA\CUDNN\v你的版本号\bin这个文件夹中,看看这里显示的子文件夹明是什么,cudnnv9.11下会显示12.9不同的版本显示不同,然后修改12.9为实际显示的数字。
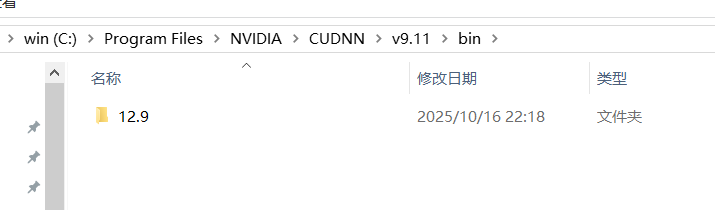
这里可能大于安装的CUDA12.8版本,不用担心,这是兼容的
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA\CUDNN\v9.11\bin\12.9C:\Program Files\NVIDIA\CUDNN\v9.11\lib\12.9C:\Program Files\NVIDIA\CUDNN\v9.11\include\12.9
完整的环境变量示意图,具体安装cuda和cudnn版本不同则显示不同
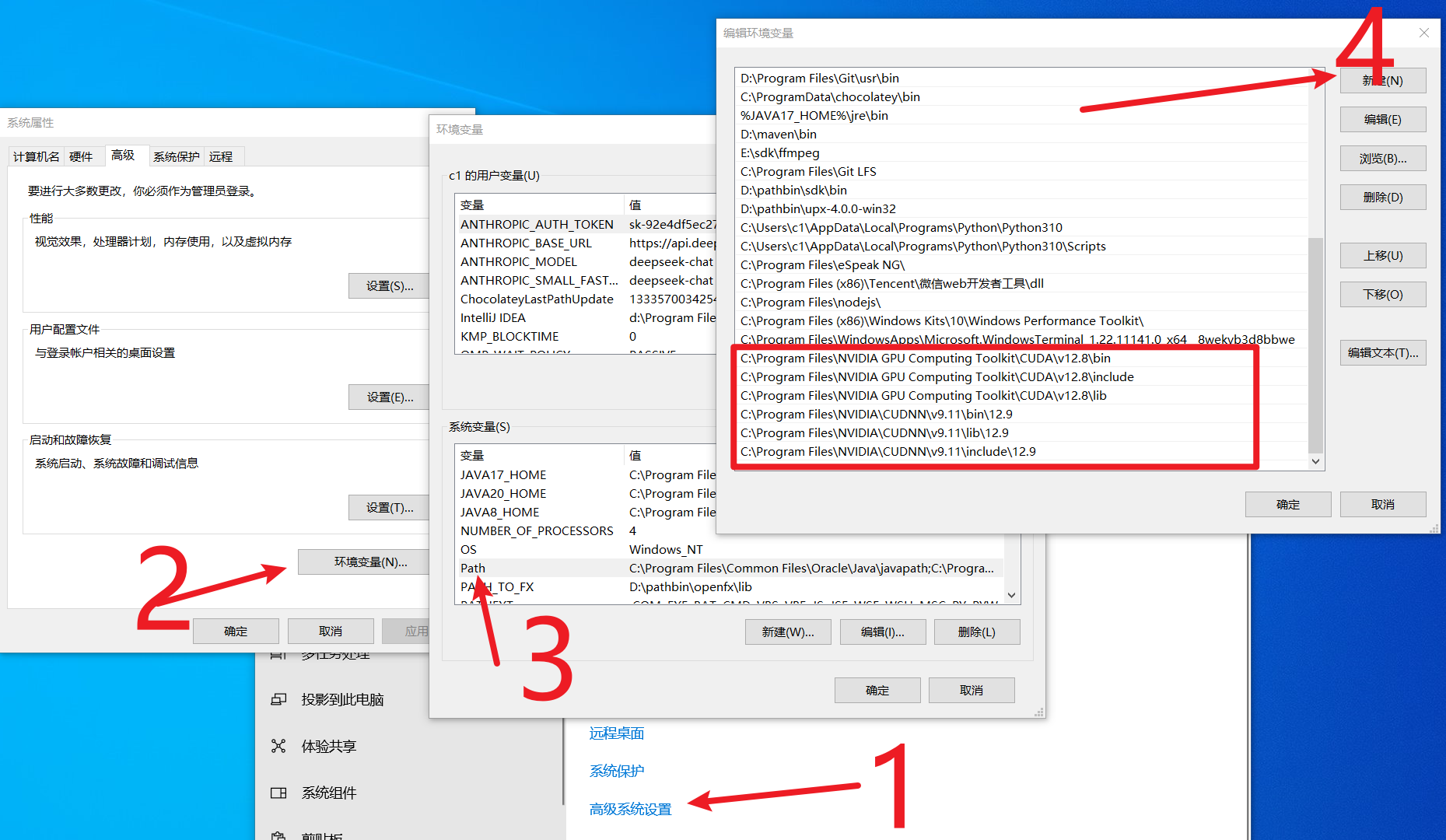
最后:大功告成!
重启下电脑。 现在 CUDA 12.8 和 cuDNN 9.11 都装好了!你可以开始运行需要 GPU 支持的程序了。如果有软件说明(比如运行 python script.py),在 CMD 里进入项目文件夹,输入对应命令试试。
有用的资源链接
- cuDNN所有版本下载地址: https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn-archive
- CUDA所有版本下载地址: https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit-archive
