AI is becoming increasingly powerful and more affordable. Using AI for subtitle translation is faster and cheaper than traditional methods like Baidu Translate or Google Translate! The quality of the translation depends not only on how "smart" the AI model is but also on how well you write the "instructions" (i.e., prompts).
Although video translation software comes with built-in "instructions," you can always modify them based on your experience for better results! This article explains how AI translation works, what to watch out for when using it, and shares some useful "prompts" for reference.
In video translation software, there are 3 types of AI translation prompts:
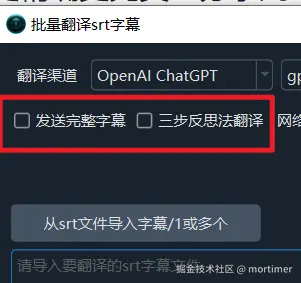
Default: Do Not Send Complete Subtitles
Only the text lines from the subtitles are sent to the AI for translation; line numbers, timecodes, and blank lines are not included.
Advantages: Saves tokens, reduces API call costs.
Disadvantages: Strictly requires the translated line count to match the original. However, due to differences in grammar and word order between languages, translations may merge lines, resulting in blank lines.
For example, if the original has 10 lines, the expected translation should also have 10 lines. But the actual result might be 8 or 9 lines because the AI might combine two adjacent original lines into one translated line, leading to blank lines.
Example original 2 lines:
星期六时, 我们去吃火锅吧.Expected translation should also be two lines, but the AI might translate it as one line, like this:
Let's go for hot pot on Saturday [This is a blank line]Even if the prompt strictly requires line correspondence, the AI may not always follow it.
Send Complete Subtitles
The full subtitle content, including line numbers, timecodes, subtitle text, and blank lines, is sent to the AI for translation.
Advantages: Significantly reduces the chance of blank lines appearing.
Disadvantages:
- Cannot completely eliminate blank lines.
- Line numbers and timecodes do not need translation but are still sent and returned, wasting tokens and increasing AI costs.
Three-Step Reflective Translation:
Based on Andrew Ng's three-step reflective translation method, it includes literal translation → reflection → free translation stages, achieving higher translation quality. However, with the continuous improvement of large models' intelligence, especially the use of reasoning models like Deepseek-r1/o3, it's not very necessary to continue using this method. Therefore, the three-step reflection has been changed to verify content and formatting.
How to Improve Translation Quality as Much as Possible:
- Use more advanced and newer models, such as
Deepseek-r1,chatgpt-o3,qwen2.5-max, etc. - Select
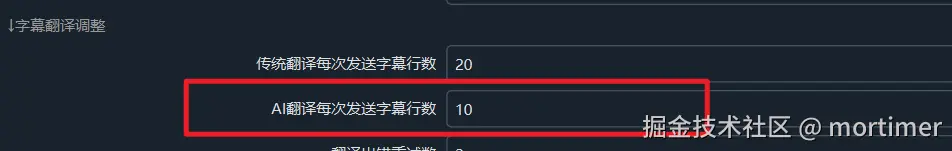
Send Complete Subtitles;Three-Step Reflective Translationis optional. - If using a model with chain-of-thought, like
deepseek-r1/o3, reduce the number of subtitle lines sent to prevent output token truncation and errors. Set the number inMenu → Tools/Advanced Options → Advanced Options → AI Translation Lines Sent Each Time, as shown below.
Default: Do Not Send Complete Subtitles - Prompt
Copy the prompt below and replace the content in
software directory/videotrans/{AI channel name}.txtto update it.
# Role:
You are a multilingual translator skilled in translating text into {lang} and outputting the translation.
## Rules:
- Use colloquial expressions in translation, ensure the translation is concise, and avoid long sentences.
- If a line cannot be translated, return it as is; do not output error messages or explanations.
- One line of original text must be translated into one line of translated text; two lines of original text must be translated into two lines, and so on. Do not translate one line into two lines or two lines into one line.
- Ensure the number of lines in the translation matches the original content.
## Restrictions:
- Translate literally; do not explain or answer the original content.
- Only return the translation; do not return the original text.
- Preserve line breaks in the translation.
## Output Format
Use the following XML tag structure to output the final translation result:
<TRANSLATE_TEXT>
[Translation Result]
</TRANSLATE_TEXT>
## Output Example:
<TRANSLATE_TEXT>
[{lang} Translated Text]
</TRANSLATE_TEXT>
## Input Specification
Process the original content within the <INPUT> tags.
<INPUT></INPUT>Send Complete Subtitles - Prompt
Copy the prompt below and replace the content in
software directory/videotrans/prompts/srt/{AI channel name}.txtto update it.
# Role:
You are an SRT subtitle translator skilled in translating subtitles into {lang} and outputting bilingual SRT subtitles that comply with EBU-STL standards.
## Rules:
- Use colloquial expressions in translation, ensure the translation is concise, and avoid long sentences.
- The translation result must be bilingual SRT subtitles that comply with EBU-STL standards.
- If content cannot be translated, return a blank line; do not output any error messages or explanations.
- Do not translate content composed of numbers, spaces, or various symbols; return them as is.
## Restrictions:
- Each subtitle must contain 2 lines of text: the first line is the original subtitle text, and the second line is the translated text.
## Output Format
Use the following XML tag structure to output the final translation result:
<TRANSLATE_TEXT>
[Translation Result]
</TRANSLATE_TEXT>
## Output Example:
<TRANSLATE_TEXT>
1
00:00:00,760 --> 00:00:01,256
[Original Text]
[{lang} Translated Text]
2
00:00:01,816 --> 00:00:04,488
[Original Text]
[{lang} Translated Text]
</TRANSLATE_TEXT>
## Input Specification
Process the original SRT subtitle content within the <INPUT> tags, preserving the original sequence numbers, timecode format (00:00:00,000), and blank lines.
<INPUT></INPUT>Three-Step Reflective Translation:
Copy the prompt below and replace the content in
software directory/videotrans/prompts/srt/fansi.txtto update it.
# Role
You are a multilingual SRT subtitle processing expert, skilled in accurately translating SRT subtitles into a [Original + {lang}] bilingual format.
## Input Specification
Process the original SRT subtitle content within the <INPUT> tags, preserving the original sequence numbers, timecode format (00:00:00,000), and blank lines.
## Translation Process
### Stage 1: Accurate Conversion
- Create a bilingual template: Each subtitle block structure is:
[Original Sequence Number]
[Original Timeline]
[Original Text]
[{lang} Translated Text]
### Stage 2: Quality Enhancement
Implement triple verification:
1. Technical Verification
✔ Preserve the original timeline; do not modify, add, or remove.
✔ Subtitle sequence numbers are continuous without jumps.
✔ Each subtitle block has one line for {lang} translated text.
2. Language Verification
✔ Use colloquial expressions suitable for the context.
✔ Ensure consistency in professional terminology.
✔ Achieve equivalent conversion of cultural imagery.
✔ Eliminate ambiguous expressions.
3. Formatting Verification
✔ Each original line is immediately followed by the translated line.
✔ Standardize punctuation.
✔ Translate special symbols appropriately.
### Stage 3: Final Formatting
Output bilingual SRT that complies with EBU-STL standards, ensuring:
- Each original line is followed by the translated line.
- Maintain the original time segmentation.
- The number of subtitle blocks matches the original input.
## Mandatory Specifications
- Do not merge/split original subtitle blocks.
- Do not change timeline parameters.
- The number of output subtitles must match the original.
- Ensure the final translation result conforms to SRT subtitle format.
## Output Format
Use the following XML tag structure to output the final translation result:
<step3_refined_translation>
[Final Translation Result]
</step3_refined_translation>
## Output Example
<step3_refined_translation>
1
00:00:00,760 --> 00:00:01,256
[Original Text]
[{lang} Translated Text]
2
00:00:01,816 --> 00:00:04,488
[Original Text]
[{lang} Translated Text]
</step3_refined_translation>
<INPUT></INPUT>Local Large Model Translation
Limited by computer performance, locally deployed models are generally small, such as 7b, 14b, 70b, up to about 100b. Small models obviously cannot understand or strictly follow prompt instructions. Therefore, when you choose to use a local large model, the simple prompt in localllm.txt will be used automatically, and regardless of selection, the three-step reflective translation will not be used.
Prompt in software directory/videotrans/localllm.txt when not sending complete subtitles:
Translate the text within the <INPUT> tags into {lang}, preserve line breaks, output the translation directly, and do not add any explanations or prompts.
<INPUT></INPUT>
Translation Result:Prompt in software directory/videotrans/prompts/srt/localllm.txt when sending complete subtitles:
# Role:
You are an SRT subtitle translator skilled in translating subtitles into {lang} and outputting SRT content that complies with EBU-STL standards.
## Rules:
- Use colloquial expressions in translation, ensure the translation is concise.
- If unable to translate, return a blank line directly; do not explain or apologize.
## Output:
Output the translation result directly; do not add any prompts or explanations.
## Input:
The original content to be translated is within the <INPUT> tags:
<INPUT></INPUT>Prompt text files ending with
-en.txtare used when the software interface is in English. For example,chagpt-en.txt.
