本文介绍了一个在线web版实时语音识别工具,它支持麦克风实时录音识别和音视频文件语音识别,并提供免费使用(无使用限制)。
语音识别技术,也称为语音转录,利用人工智能将音频或视频中的语音转换为文本。这项技术在诸多领域都有广泛应用,例如会议记录、语音助手、字幕生成等等。
目前,语音识别主要有两种方式:
1. 基于离线模型的语音识别:
这种方式需要在本地计算机上部署语音识别模型。一个流行的开源方案是OpenAI Whisper。下载其大型模型(例如large-v2)后即可离线使用,无需联网且无需付费。
然而,这种方法需要较强的计算资源(例如强大的显卡),否则识别速度会很慢,准确率也会下降。
2. 基于在线API的语音识别:
一些公司提供在线语音识别API服务,例如字节跳动和OpenAI。
用户只需将音频数据上传到API,即可获得转录结果。
这种方式无需本地硬件资源,速度快且准确率高,但需要支付一定的费用。
实时语音识别
以上两种方式主要针对已有的音频或视频文件。那么,如何对麦克风实时录制的音频流进行实时转录呢?例如,如何在会议中实时记录发言并将其转换为文字?
实时语音识别与文件转录的原理相似,但技术难度更高。它需要:
- 实时数据流处理: 持续不断地从麦克风接收音频数据。
- 数据切片与识别: 将连续的音频流切分成较小的片段,并逐个进行识别。
- 结果整合与纠错: 将各个片段的识别结果整合起来,并进行纠错,以提高最终转录的准确性。这通常需要更复杂的算法来处理语音的停顿、重叠等情况。
- 最小延时: 需要尽可能减少从音频输入到文本输出的延迟,以保证实时性。
技术原理及使用介绍
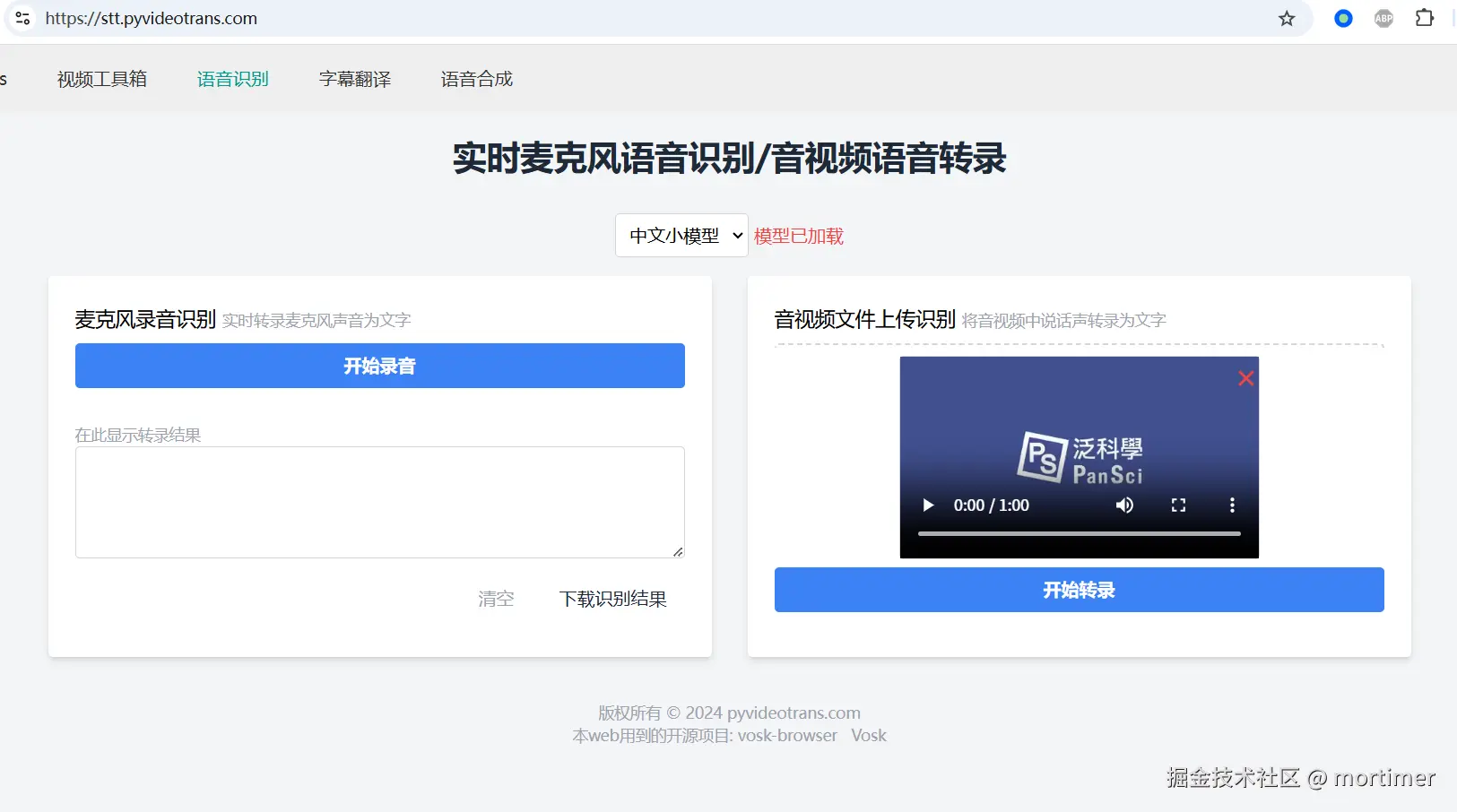
- 麦克风实时录音识别: 使用麦克风实时录制音频,并实时进行转录。
- 音视频文件语音识别: 支持上传本地音频或视频文件进行转录。
技术原理:
轻量级语音识别模型 (Vosk): 为了在浏览器环境下运行,我们采用了体积小巧的Vosk语音识别模型。虽然它的准确率相对较低,但可以有效地降低资源占用,保证在浏览器中流畅运行。
本地音频处理 (ffmpeg.wasm): 利用ffmpeg.wasm在用户的浏览器内进行音视频文件的处理和语音提取,无需将音频数据上传到服务器。
客户端模型加载: 语音识别模型下载后在浏览器内存中运行。这限制了我们使用更大、更精准的模型,只能选择较小模型以避免浏览器崩溃。即使用户的电脑性能强大,由于服务器带宽的限制,目前也不支持大型模型。
使用方法
- 模型加载: 使用前,请根据需要加载中文或英文模型。
- 麦克风识别: 点击左侧区域的按钮,开始使用麦克风进行实时录音和识别。识别结果将实时显示在文本框中。
- 文件识别: 在右侧区域选择本地音频或视频文件,工具将使用ffmpeg.wasm进行本地处理并进行语音识别。结果显示在文本框中。
- 结果下载: 可将转录后的文本下载为TXT文件。
注意事项
- 互斥功能: 麦克风实时识别和文件识别功能不能同时使用。
- 本地处理: 模型和音频处理都在用户的浏览器本地进行。
- 语言支持: 目前仅支持中文和英文语音识别。
- 性能限制: 由于使用了轻量级模型,识别准确率可能不如大型模型。
常见问题
- Q: 识别准确率低怎么办? A: 我们使用了轻量级模型以保证浏览器兼容性和运行速度。如果您需要更高的准确率,建议下载 pyVideoTrans 本地使用large-v2模型。
- Q: 支持哪些语言? A: 目前仅支持中文和英文。
- Q: 为什么速度慢? A: 这可能是由于网络状况、浏览器性能或计算机资源不足导致的。
- Q: 可以上传多大的文件? A: 文件大小受限于浏览器内存和处理能力。
